How to Log AWS IoT Core Alarms to PostgreSQL
Open Automation Software can be configured to connect to AWS IoT Core using the AWS IoT Gateway connector, trigger alarms and log them to a PostgreSQL database. This guide walks you through downloading and installing OAS, configuring an AWS IoT Gateway connector, configuring tags, setting an alarm limit and configuring alarm logging to PostgreSQL.
For this guide on how to log AWS IoT Core alarms to PostgreSQL you will need:
- An AWS IoT Core instance and access credentials
- A PostgreSQL server and database
1 - Download and Install OAS
If you have not already done so, you will need to download and install the OAS platform.
Fully functional trial versions of the software are available for Windows, Windows IoT Core, Linux, Raspberry Pi and Docker on our downloads page.
On Windows, run the downloaded setup.exe file to install the Open Automation Software platform. For a default installation, Agree to the End User License Agreement and then click the Next button on each of the installation steps until it has completed.
If you'd like to customize your installation or learn more, use the following instructions:
The OAS Service Control application will appear when the installation finishes on Windows.
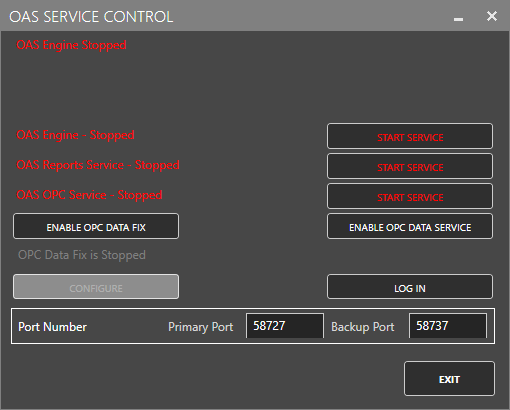
Click on each START SERVICE button to start each of the three OAS services.
2 - Configure OAS
Configure OAS is the main application used to configure local and remote OAS instances.

From your operating system start menu, open the Configure OAS application.
Select the Configure > Tags screen.
Important
If this is the first time you have installed OAS, the AdminCreate utility will run when you select a screen in the Configure menu. This will ask you to create a username and password for the admin user. This user will have full permissions in the OAS platform.
For further information see Getting Started - Security.
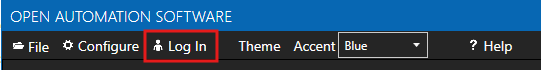
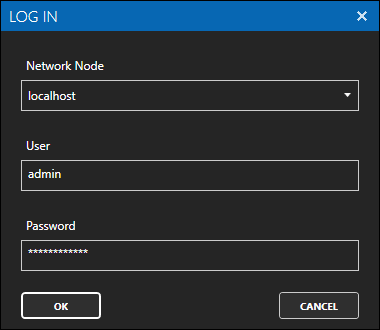
If this is the first time you are logging in, you will see the AdminCreate utility. Follow the prompts to set up your admin account. Otherwise, select the Log In menu button and provide the Network Node, username and password.
Info
In this guide you will use the Configure OAS application to configure the local Network Node which by default is localhost.
If you have installed OAS on a remote instance you can also connect to the remote instance by setting the relevant IP address or host name in the Network Node field.
3 - Create Subscriber Thing in AWS IoT Core
In this step you will create a Thing in the AWS IoT Core service and the required certificate and policies for subscribing to messages sent by AWS IoT Core. This represents your connection and security settings between AWS IoT Core and OAS.
Login to the AWS Console and select the AWS IoT service.
Under the Manage and All Devices menu select Things.
Click on the Create things button to start the create new things wizard.
Select Create single thing and click on the Next button.
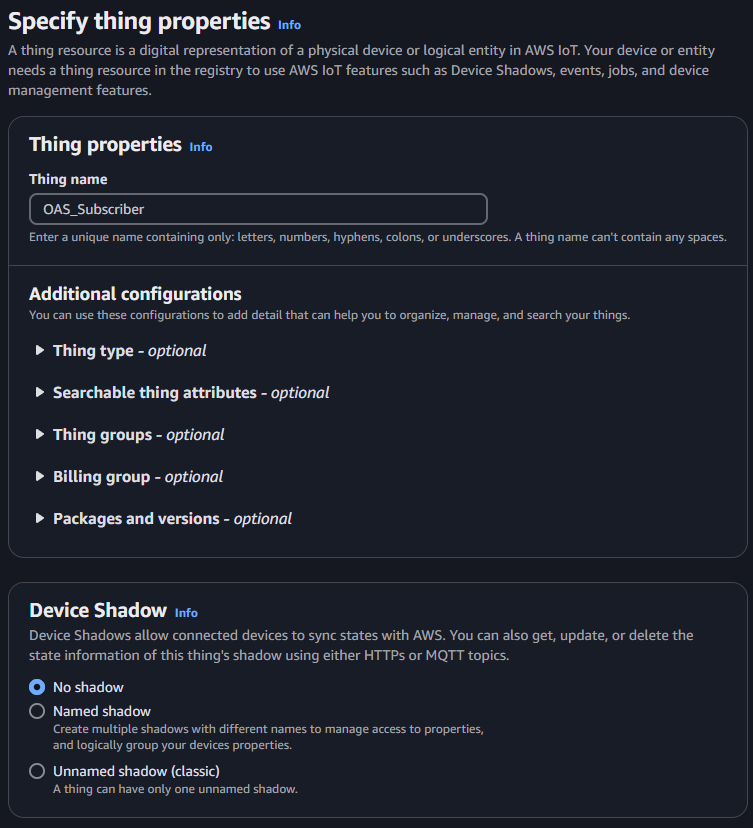
Set the Thing name to OAS_Subscriber and click on the Next button.
Leave the default option to generate device certificate automatically and click on the Next button.
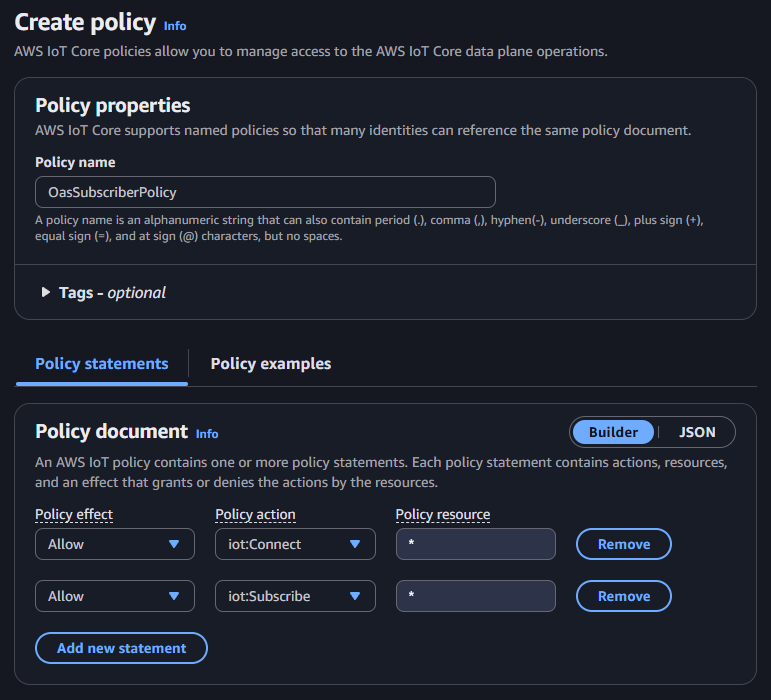
Select the Create policy button. This will open a new browser tab or window.
Set the Policy name to OASSubscriberPolicy. The policy will need to allow the iot:Connect and iot:Subscribe actions. For the purpose of this guide the policy will allow all resources using the * wildcard.
Important
For security best practices in production systems you should always restrict your policy to the client ID and AWS resource name (ARN) that represents your region, account and topic paths.
Go back to the create thing wizard and select the OASSubscriberPolicy. Click on the Create thing button.
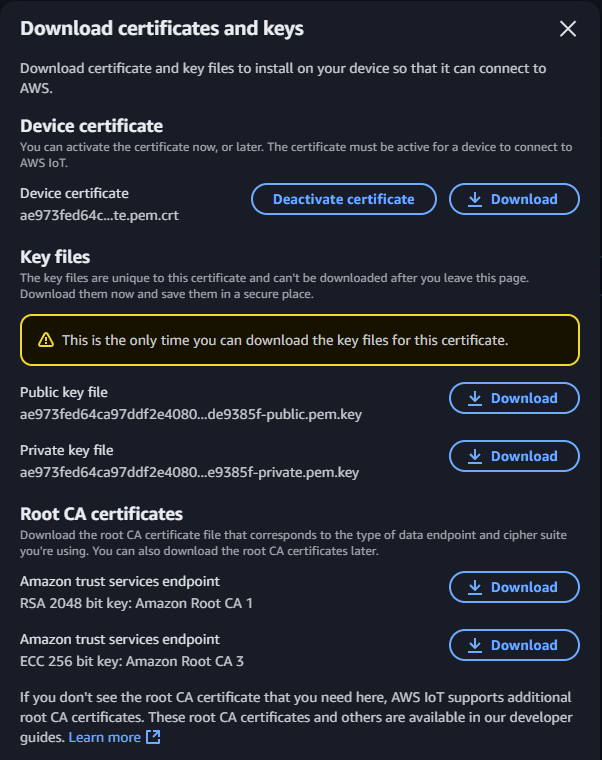
You will see a window relating to certificates. Download the device certificate, the public key file, the private key file and one of the Root CA certificates. You should keep these files in a folder with limited permissions. You'll need them when configuring the AWS IoT Core subscriber in the OAS platform.
4 - Configure AWS IoT Core Subscriber
In the following steps you will create and configure an AWS IoT Core Subscriber for subscribing to tag values.
To determine the AWS IoT Core endpoint you will need to login to the AWS console and select the AWS IoT service. Select the Domain configurations menu.
If you don't already have a domain name use the Create domain configuration button to create one. You will need to take a note of the Domain name property, which represents your AWS IoT Core broker endpoint.
In the Configure OAS application, select Configure > Drivers from the top menu.
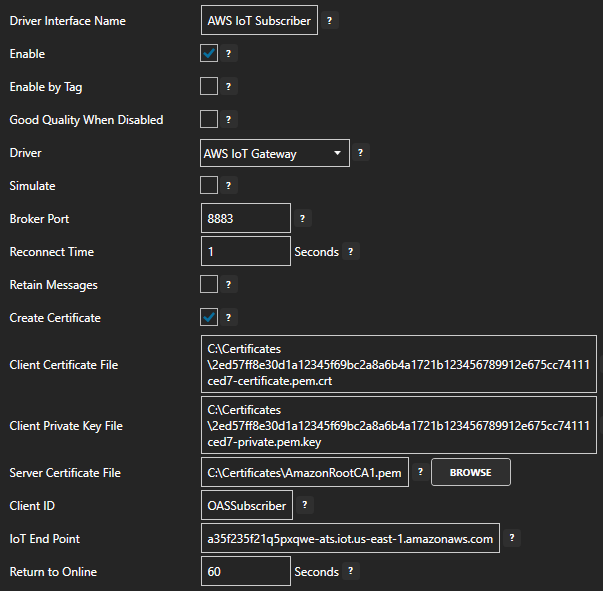
Enter a meaningful Driver Interface Name to give this driver interface instance a unique name (for example AWS IoT Subscriber).
Ensure the following parameters are configured:
- Driver: AWS IoT Gateway
- BrokerPort: 8883
- Create Certificate: Select this if running Windows
- Client Certificate File: The device certificate pem.crt file from the previous section
- Client Certificate Key File: The private pem.key file from the previous section
- Server Certificate File: The Root CA pem file from the previous section
- Client ID: OASSubscriber
- IoT End Point: This is your AWS Iot Core endpoint from step 2 above
Info
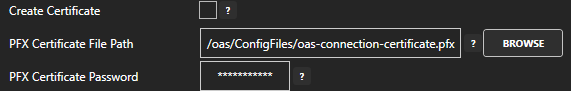
If you are using Linux, you can generate a PFX certificate using OpenSSL.
openssl pkcs12 -export \ -out oas-connection-certificate.pfx \ -inkey 2ed57ff8e30d1a12345f69bc2a8a6b4a1721b123456789912e675cc74111ced7-private.pem.key \ -in 2ed57ff8e30d1a12345f69bc2a8a6b4a1721b123456789912e675cc74111ced7-certificate.pem.crt \ -certfile AmazonRootCA1.pemYou can then use the generated certificate and password in your AWS IoT Gateway driver configuration:
Click the ADD DRIVER button on the left hand side to add this driver configuration. Once added, the driver interface name should appear in the list of drivers.
5 - Assign AWS IoT Gateway as Tag Data Source
You will now set the Tag's data source to the AWS IoT Subscriber interface that you created previously.
Select the Tag that will source data from the AWS IoT Core data source.
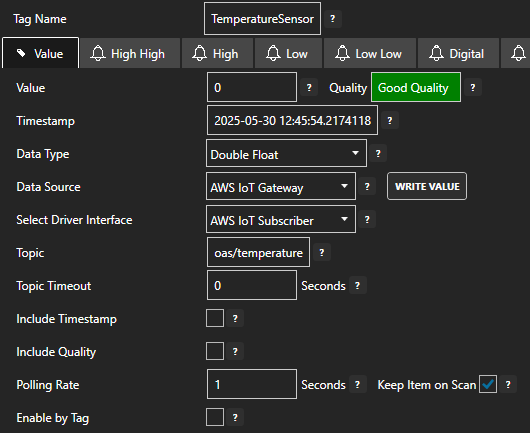
Set the following properties:
- Data Source: AWS IoT Gateway
- Select Driver Interface: AWS IoT Subscriber
- Topic: oas/temperature
Click on the Apply Changes button to apply the changes.
Login to the AWS Console and select the AWS IoT service.
Under the Test menu select MQTT test client and then select the Publish to a topic tab.
In the Topic name specify oas/temperature.
In the Message payload enter a value and then click on the Publish button.
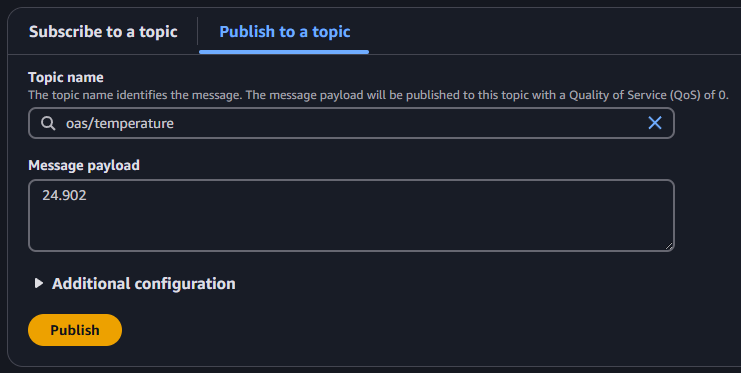
Check that the quality status is Good Quality and you can see the value.

6 - Set Tag Alarm Limit
Select the Tag where you want to enable the alarm limit.

Select the High tab to open the high alarm limit configuration screen.
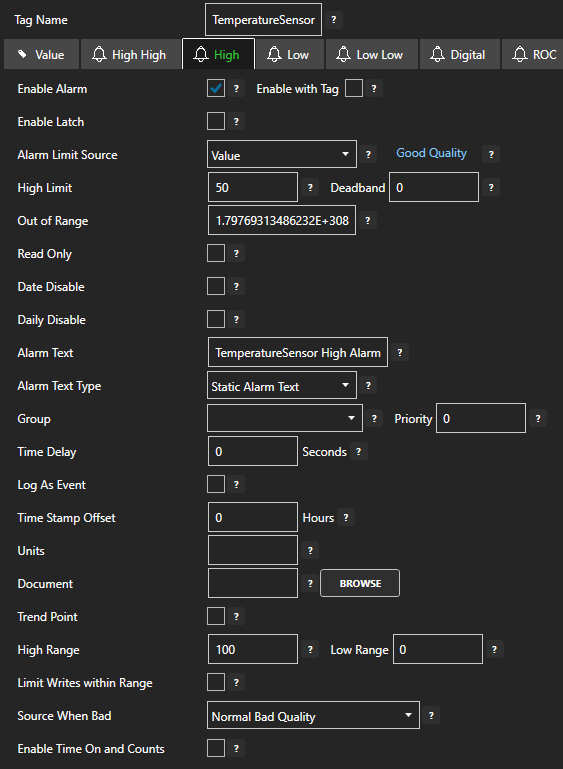
Configure the following setting to enable the high alarm limit:
- Tick the Enable Alarm checkbox
- Set the High Limit value to your desired value threshold for triggering the alarm
Optionally you can also configure:
- Alarm Text to customize the alarm text that will be shown. You can combine this with different Alarm Text Type settings in order to prepend, append, overwrite or replace the alarm text with a calculation.
- Group to categorize the alarm into a specific group. This can be used to filter alarms when configuring logging and notifications.
- Priority to order and apply a specific priority to each alarm.
- Time Delay which suppresses the alarm for the specified amount of time after it is triggered.
- Log As Event which means the alarm will only be recorded as a single instance without an acknowledgement state.
7 - Configure Alarm Logging
You will now configure alarm logging to a PostgreSQL database.
Select Configure > Alarm Logging from the top menu.
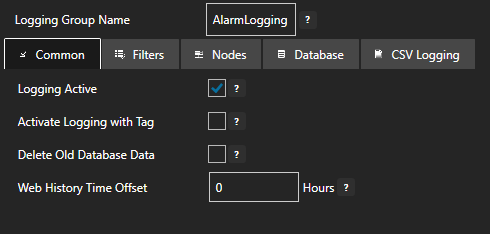
Enter a meaningful Logging Group Name to give this alarm logging group a unique name. An alarm logging group is defined by a specified filter, OAS node list (default localhost) and database connection or CSV file configuration.
On the Common tab leave all the default values which will ensure the logging group is active.
On the Filters tab you can customize which alarms should be included in your logging. This includes filtering by:
- Alarm state
- Alarm priority
- Alarm type
- Alarm group
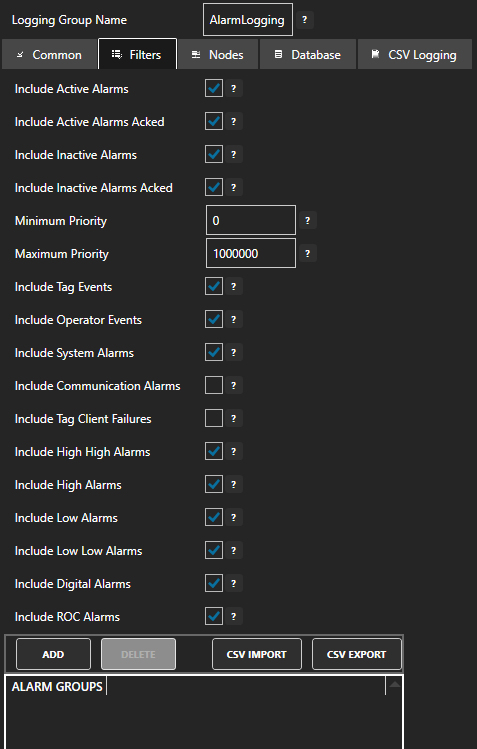
On the Nodes tab you can leave the default settings if you only want to include alarms generated on the local node. Once you add the alarm group the localhost node will be added to the list automatically.
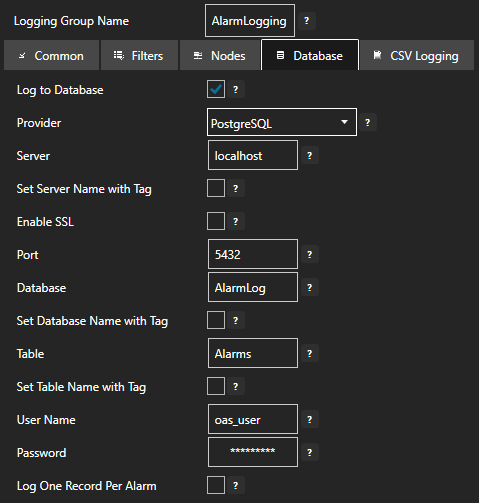
On the Database tab you will configure the database type and connection parameters:
- Tick the Log to Database checkbox to enable logging to a database
- Set Provider to PostgreSQL
- Set Server to your PostgreSQL server (e.g., localhost)
- Set Database to AlarmLog
- Set Table to a table name such as Alarms
- Set User Name to a user with permissions to manage the AlarmLog database
- Set Password to the user password
Click on the ADD GROUP button to add the alarm logging group. Once added, the alarm logging group name should appear in the list of logging groups.
Your alarm logging group is now active.
8 - Save Changes
Once you have successfully configured your OAS instances, make sure you save your configuration.
On each configuration page, click on the Save button.
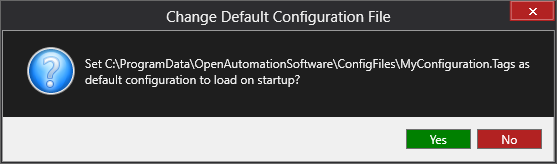
If this is the first time you are saving the configuration, or if you are changing the name of the configuration file, OAS will ask you if you want to change the default configuration file.
If you select Yes then OAS will make this configuration file the default and if the OAS service is restarted then this file will be loaded on start-up.
If you select No then OAS will still save your configuration file, but it will not be the default file that is loaded on start-up.
Important
Each configuration screen has an independent configuration file except for the Tags and Drivers configurations, which share the same configuration file. It is still important to click on the Save button whenever you make any changes.
For more information see: Save and Load Configuration
Info
- On Windows the configuration files are stored in C:\ProgramData\OpenAutomationSoftware\ConfigFiles.
- On Linux the configuration files are stored in the ConfigFiles subfolder of the OAS installation path.