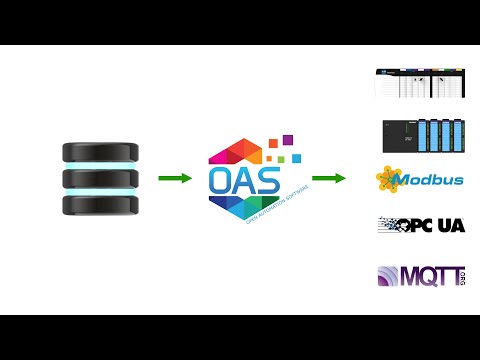
CHOOSE CONNECTORS
OAS connects to all commonly used industrial and business data sources. Select a data source to learn more about its setup:
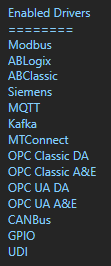
- Configure Allen Bradley Driver Interface
- Configure Tags
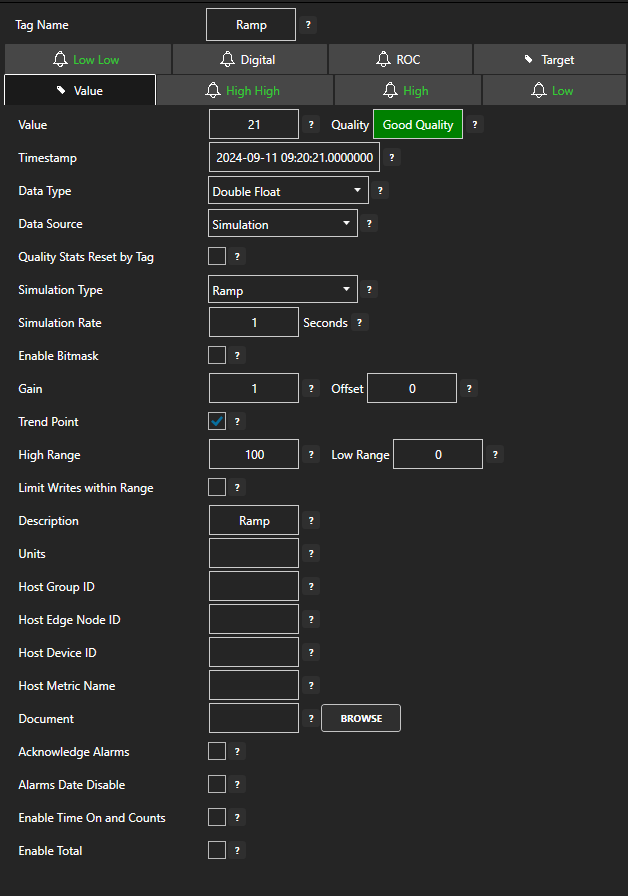
OAS provides multiple ways to configure tags including:- Automated ‘One Click’ setup
- manual configuration
- CSV Import
- Full programmatic access to OAS tags. Use the OAS Systems component in Visual Studio to programmatically modify Tag and Tag Groups.
- Configure AWS IoT Driver Interface
- Configure Tags
- Configure Siemens Driver Interface
- Configure Tags
OAS provides multiple ways to configure tags including:- manual configuration
- CSV Import
- Full programmatic access to OAS tags. Use the OAS Systems component in Visual Studio to programmatically modify Tag and Tag Groups.
- Configure Modbus Driver Interface
- Configure Tags
OAS provides multiple ways to configure tags including:- manual configuration
- CSV Import
- Full programmatic access to OAS tags. Use the OAS Systems component in Visual Studio to programmatically modify Tag and Tag Groups.
- Configure MQTT Driver Interface
- Configure Tags
OAS provides multiple ways to configure tags including:- manual configuration
- CSV Import
- Full programmatic access to OAS tags. Use the OAS Systems component in Visual Studio to programmatically modify Tag and Tag Groups.
- Configure MTConnect Driver Interface
- Configure Tags
OAS provides multiple ways to configure tags including:- manual configuration
- CSV Import
- Full programmatic access to OAS tags. Use the OAS Systems component in Visual Studio to programmatically modify Tag and Tag Groups.
- Configure Sparkplug B Driver Interface
- Configure Tags
OAS provides multiple ways to configure tags including:- manual configuration
- CSV Import
- Full programmatic access to OAS tags. Use the OAS Systems component in Visual Studio to programmatically modify Tag and Tag Groups.
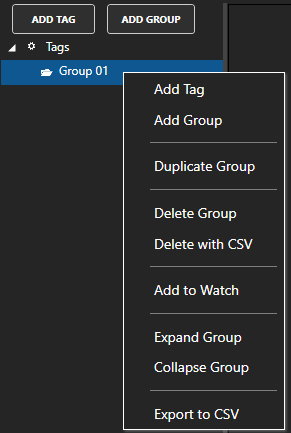
- Manual Configuration – Add Tags
- CSV Import
- Full programmatic access to OAS tags. Use the OAS Systems component in Visual Studio to programmatically modify Tag and Tag Groups.
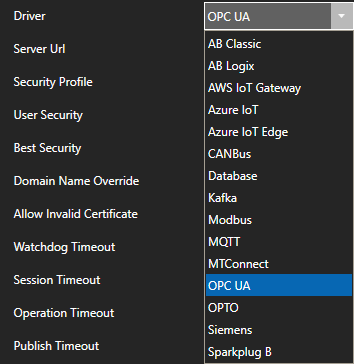
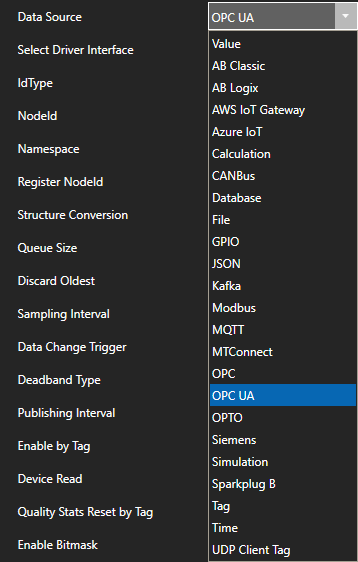
- Configure OPC UA Driver Interface
- Configure Tags
OAS provides multiple ways to configure tags including:- manual configuration
- CSV Import
- Full programmatic access to OAS tags. Use the OAS Systems component in Visual Studio to programmatically modify Tag and Tag Groups.
Connect to OPC Clients like WinCC Cimplicity, RS View etc. by making OAS tags available as OPC items. Sample client Add OPC items from OPC Server Our OPC server makes OPC items to connect to
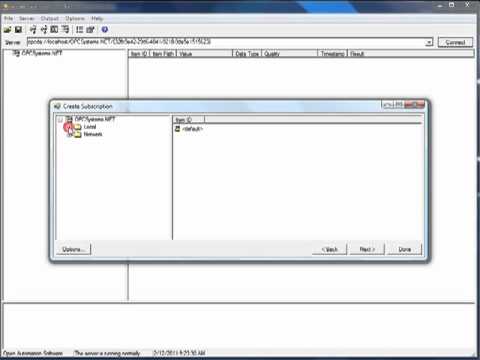
- Create a subscription to an OPC Item
- CSV Import
- Full programmatic access to OAS tags. Use the OAS Systems component in Visual Studio to programmatically modify Tag and Tag Groups.
Connect OAS local and remote tags to OPC UA Clients.
Use the OAS Excel Tag Browser application to browse OAS tags and enable OAS read / write values from/to an Excel workbook
- Setup read functions in Excel
- Full programmatic access to OAS tags. Use the OAS Systems component in Visual Studio to programmatically modify Tag and Tag Groups.
Use the Configure Recipes interface to configure data transfer from databases to OAS data sources. The data target can be from local or remote OAS Services of Tag Parameter Values. Execution can be continuous or event driven from a Tag Parameter value, or at a specific time of day. The database providers can be SQL Server, Access, Oracle, mySQL, PostgreSQL, InfluxDB, MongoDB, MariaDB, SQLite, and more.
Add real-time read data to a C#, C++, or Visual Basic.NET WPF, WinForm, or Windows Service application. It is a very powerful method to make any data from a .NET application become a realtime data source.
Read local and remote data from the Open Automation Software realtime database tags where the data source is a web application or web service. You can make use of the OAS products Web HMI, Web Trend, Web Alarm or for greater control use the OAS REST API or the HTTP API.
- WEB HMI Programming Reference
- Web Trend Programming Reference
- Web Alarm Programming Reference
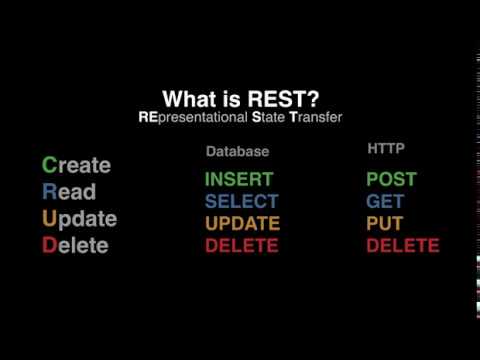
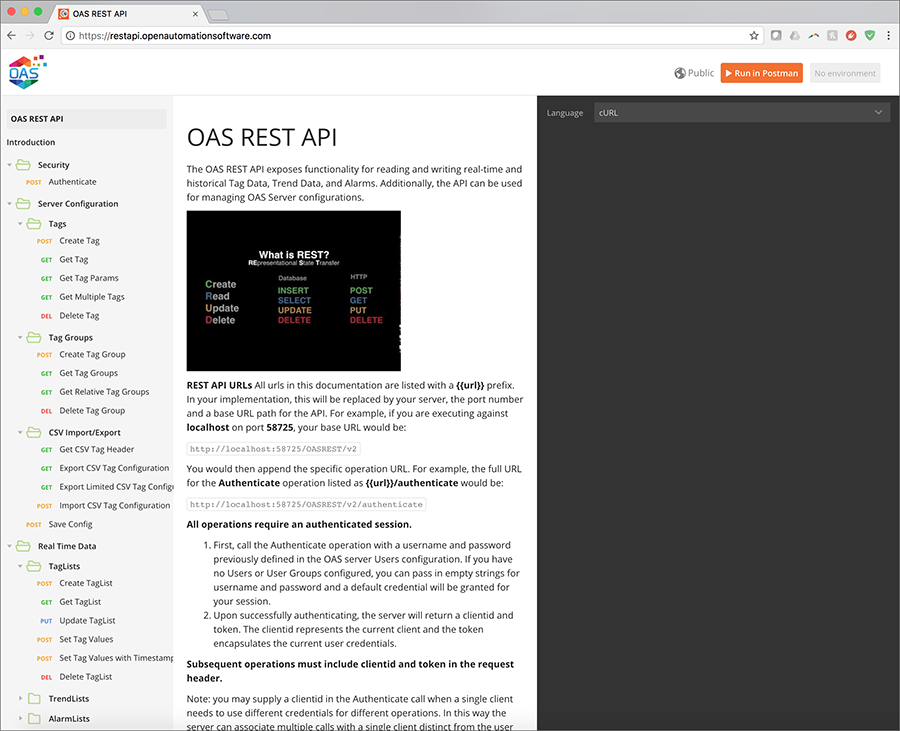
- REST API
- HTTP API (JSON over HTTP) Programmatic Interface Any client that can make HTTP calls using JSON data structures can call the API to perform read functions.
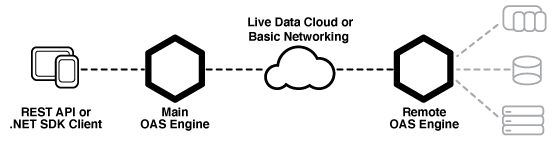
Create cross platform communication drivers to deploy locally or remotely with custom configuration and optional automated setup.
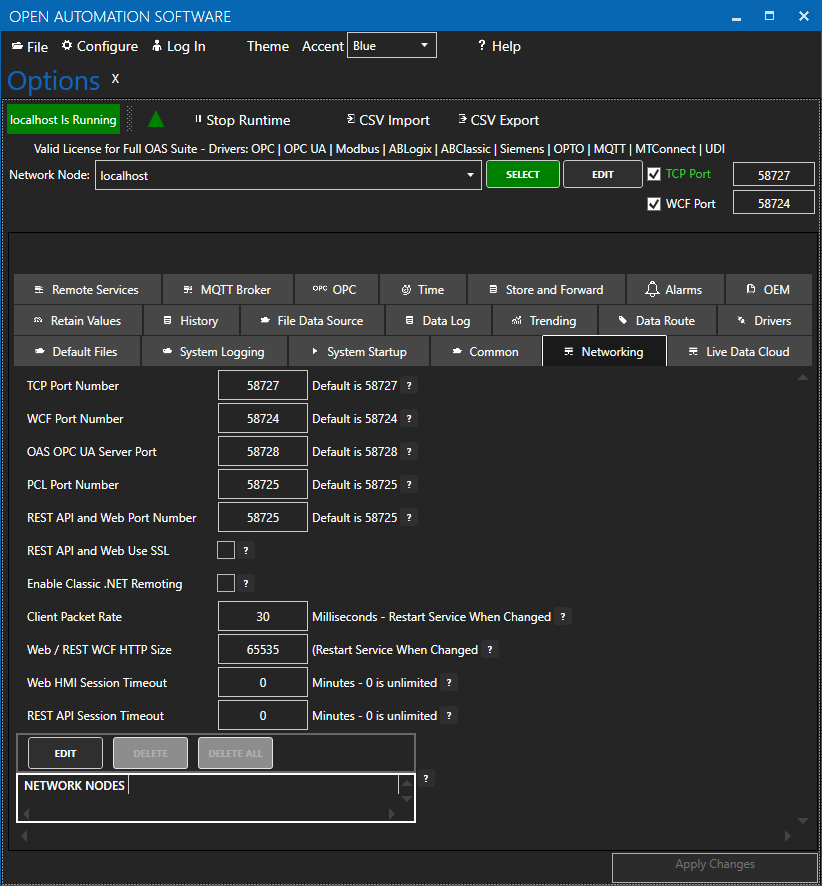
Connectors are configured using the OAS Configuration tool or the OAS APIs.
Connectors Overview
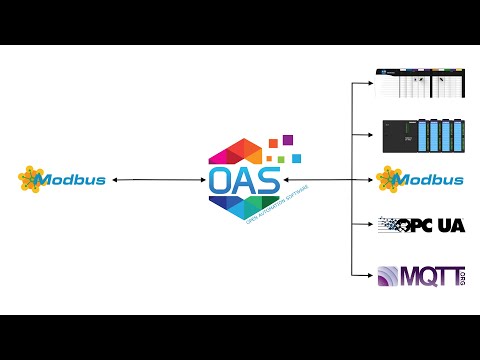
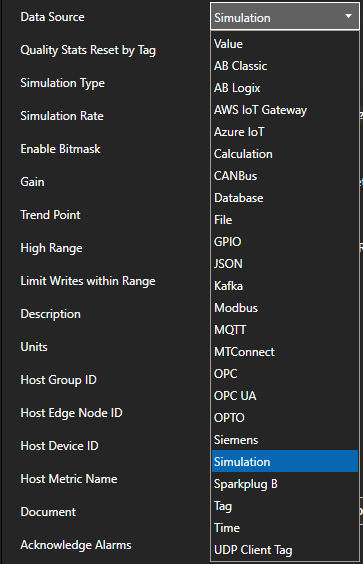
Modbus Data Source
If your data source is a Modbus slave device with either Ethernet or Serial physical interface with Modbus TCP, Modbus RTU, or Modbus ASCII protocol use Configure-Drivers and Configure-Tags to setup communications to the devices.
Refer to Getting Started Modbus under System Configuration-Tags for a quick guide on how to set it up.
Allen Bradley Data Source
If your data source is an Allen Bradley controller use Configure-Drivers and Configure-Tags to setup communications to the devices.
Refer to Getting Started Allen Bradley under System Configuration-Tags for a quick guide on how to set it up.
Siemens Data Source
If your data source is a Siemens controller use Configure-Drivers and Configure-Tags to setup communications to the devices.
Refer to Getting Started Siemens under System Configuration-Tags for a quick guide on how to set it up.
MQTT Data Source
If your data source is MQTT use Configure-Drivers and Configure-Tags to setup communications to the devices.
Refer to Getting Started MQTT under System Configuration-Tags for a quick guide on how to set it up.
Sparkplug B Data Source
If your data source is a Sparkplug B Edge of Network Node use Configure-Drivers and Configure-Tags to setup communications to the devices.
Refer to Getting Started Sparkplug B Host App under System Configuration-Tags for a quick guide on how to set it up.
Note: OAS can also act as an Edge of Network Node as a data destination to publish data to a Host and receive Metric values with a NCMD or DCMD command.
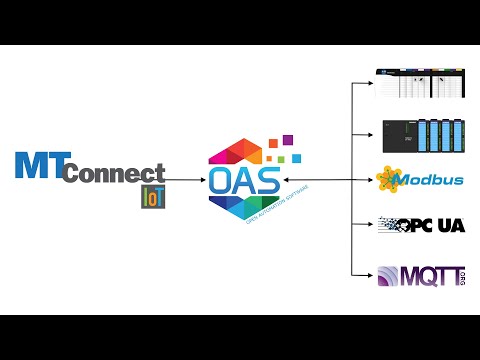
MTConnect Data Source
If your data source is MTConnect use Configure-Drivers and Configure-Tags to setup communications to the devices. The MTConnect driver will automatically generate OAS Tags based on the MTConnect device information received from the Live Data Url.
Refer to Getting Started MTConnect under System Configuration-Tags for a quick guide on how to set it up.
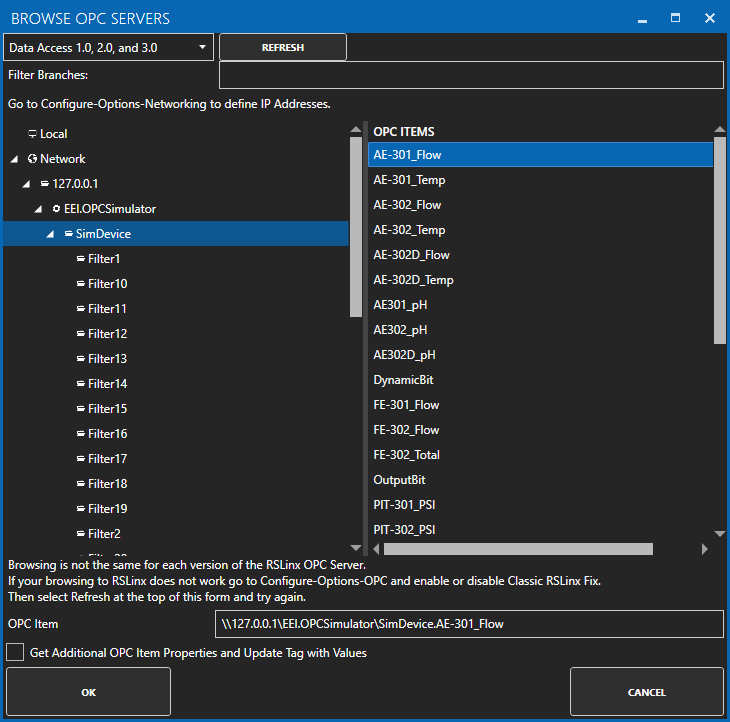
OPC Server Data Source
If your data source is an OPC Server use Configure-Tags to define a Tag with a Data Source of OPC Item or you can use DirectOPC from the database.
For a detailed presentation of connecting to OPC Servers view the following video:
View Getting Started OPC Server and also the reference for Tags in this help file.
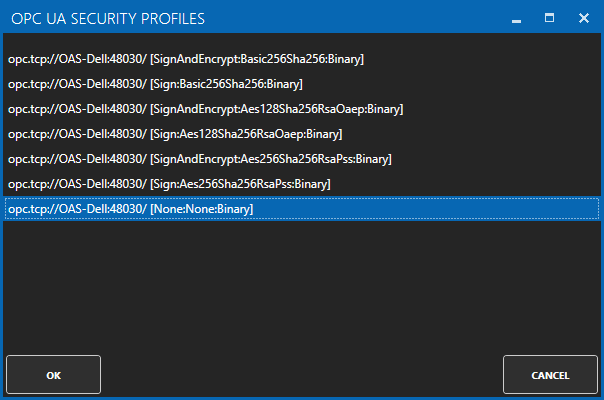
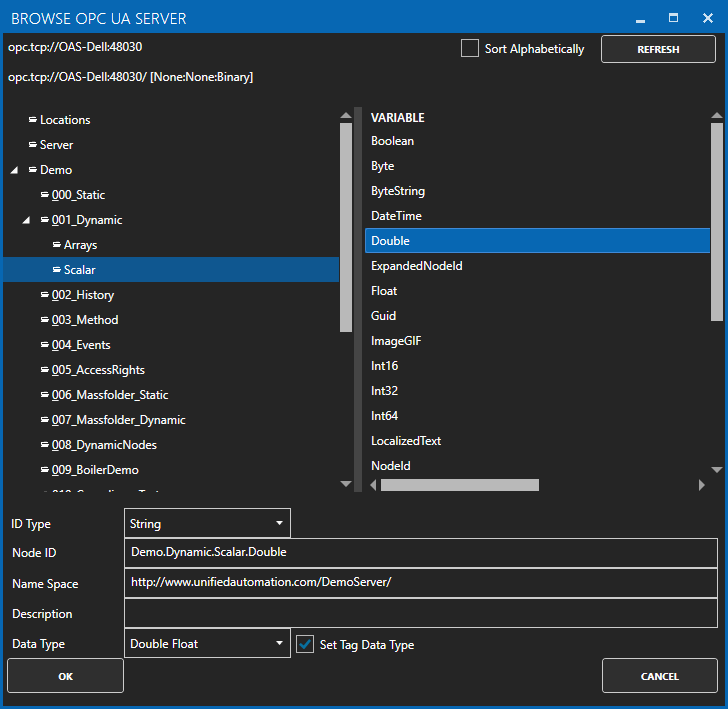
OPC UA Server Data Source
If your data source is an OPC UA Server use Configurat-Drivers and Configure-Tags to define a Tag with a Data Source of OPC UA.
View Getting Started OPC UA Server and also the reference for Tags in this help file.
OPC Clients Data Source
If your data will be coming directly from an OPC Client you can implement the OPC Client Connector product feature which supports local and remote OPC Clients without DCOM.
View the following 4 minute video on OPC Client Connector:
View the OPC Client Connector Quick Start and reference on OPC Client Connector in this help file.
OPC UA Clients Data Source
If your data will be coming directly from an OPC UA Client you can implement the OPC Client Connector product feature which supports local and remote OPC UA Clients to connect to local and remote OAS Tags.
View the Getting Started – OPC UA Client reference.
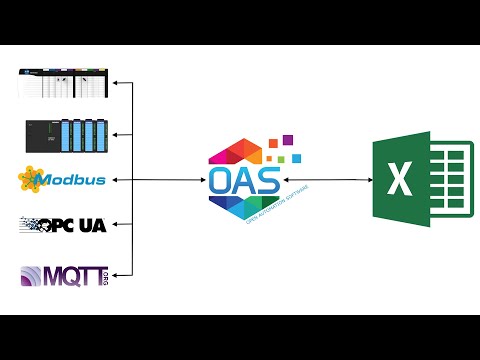
Microsoft Excel Data Source
You can use Microsoft Excel as a data source for Open Automation Software with the product feature OAS Excel Connector.
View the following video on OAS Excel Connector:
View Getting Started OAS Excel Connector and reference on OAS Excel Connector in this help file.
Databases Data Source
You can use SQL Server, Oracle, Access, and MySQL as a data source for Open Automation Software with the product feature Recipe.NET.
View the following 27 minute video on Recipe.NET:
View the Getting Started Recipe.NET and reference on Recipe.NET in this help file.
.NET Applications Data Source
By implementing a Windows Service, WinForm application, HTML application and WPF application as a data source the type data to be able to share with Open Automation Software is almost unlimited. This is implemented with the data component from OPC .NET WinForm HMI .NET.
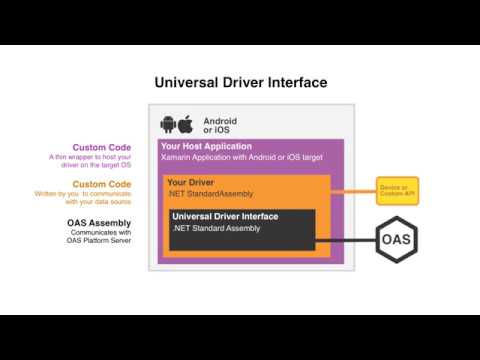
Universal Driver Interface
Create your own driver for OAS that can be deployed either locally or remotely, even for cross platform support.
See the UDI Technical Overview for an introduction and follow the Create a Driver help topic for step by step instructions.
For an overview of a UDI example view the following video:
Calculations
How to setup math equations and logic as a Data Source with the built-in Calculation engine for all products.
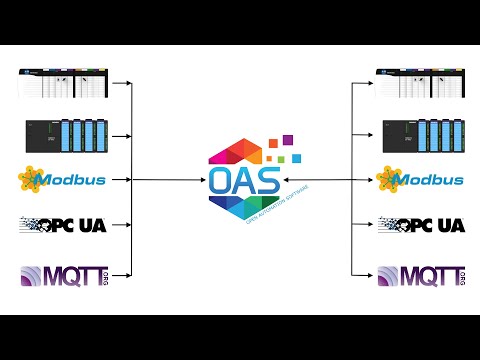
Data Route – Data Transfer
How to setup automated data transfer from one source to another locally or over on your LAN, WAN, and Internet.