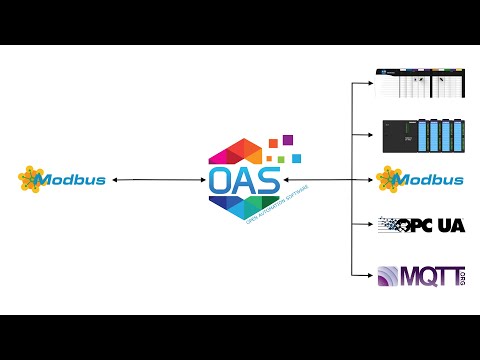
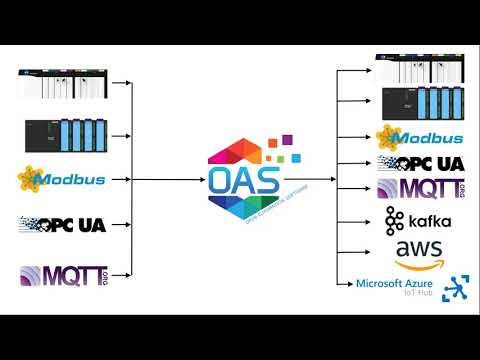
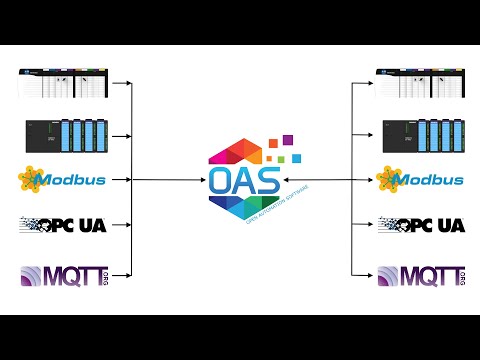
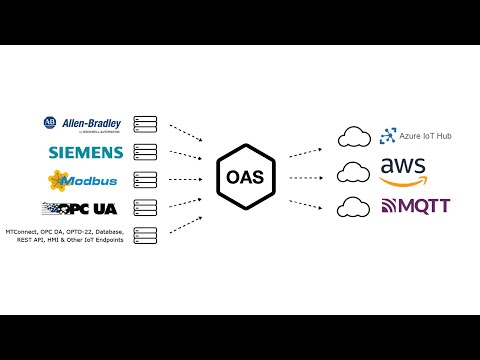
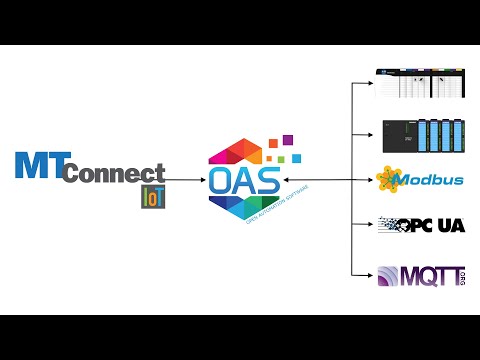
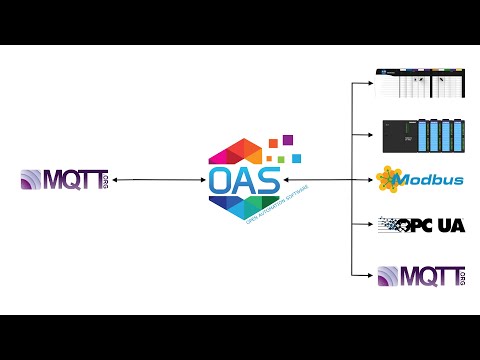
Open Automation Software can be used to transfer data from Modbus TCP, Modbus RTU, and Modbus ASCII devices to OPC Servers, locally or over a network. This tutorial walks you through downloading and installing OAS, configuring a Modbus driver, configuring Modbus and OPC tags and implementing Data Route.
Step 1. Download and Install the Open Automation Software and Start the OAS Service
If you have not already done so, you will need to download and install the OAS platform. Fully functional trial versions of the software are available for Windows, Windows IoT Core, Linux, Raspberry Pi and Docker on our downloads page.
On Windows run the downloaded Setup.exe file to install one or more of the Open Automation Software features. Select the default Typical installation if you are not sure what features to use or the Custom installation if you want to save disk space on the target system. When prompted agree to the End User License Agreement to continue the installation.
For more detailed instructions and video tutorials, visit the installation guide for your system:
Windows Installation | Linux Installation | Raspberry Pi Installation | Dockers Installation
The OAS Service Control application will appear when the installation finishes on Windows. Use this application to start the 3 Services. Run the Configure OAS application on Windows and select Configure-Tags; if the first time running, the AdminCreate utility will run to create an Administrator login as shown in Step 1 of Getting Started – Security.
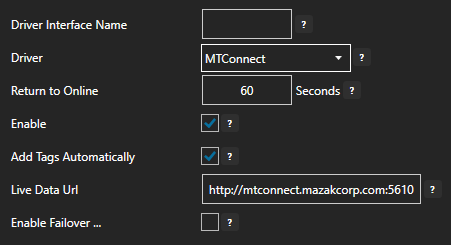
Step 2. Configure Your Modbus Data Source
- First, you will need to open the Configure OAS application from the program group Open Automation Software.
- Select Configure >> License from the top menu and verify that Modbus is one of the available Drivers in the lower left of the form. The demo license will have this by default. If you do not see Modbus available, contact support@openautomationsoftware.com to update your license.
- Select Configure >> Drivers from the top menu.
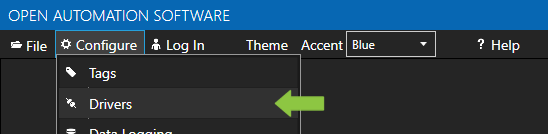
- Select localhost or the remote service you wish to modify with the Select button to the right of the Network Node list.

- The Configure Drivers Screen will appear. Select Modbus from the Driver dropdown box.
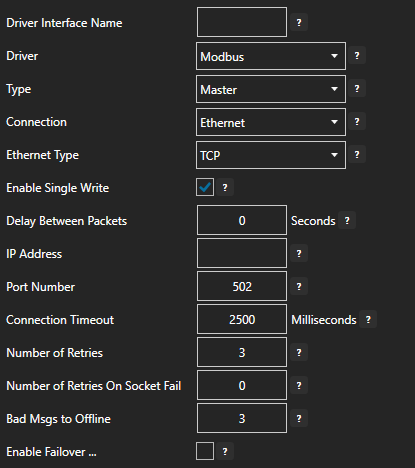
- Enter a meaningful Driver Interface Name that you will refer to this physical connection when defining Tags with a Modbus Data Source.
- Specify the Connection as Ethernet or Serial.
- Specify the Modbus Type as Master or Slave. Master will be used when communicating to a Modbus device. Slave will be used when other Modbus masters will be communicating to OAS.
- When setting up a Slave interface over Ethernet set the IP Address to the computer IPv4 IP address or network node name if the master is on a remote PC. You can also use 127.0.0.1 or localhost if the Modbus master will be on the same computer.
For more detailed instructions on configuring your Modbus data source, click here to see our Getting Started Modbus tutorial or watch the video tutorial below:
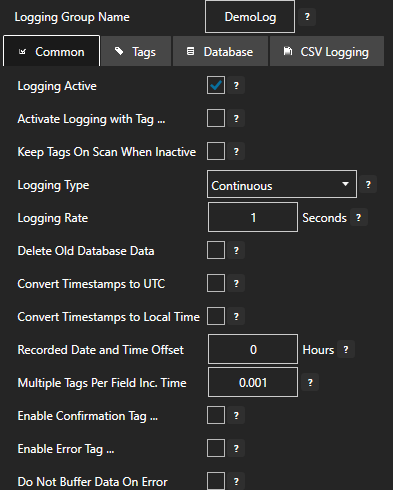
Step 3. Configure Your Modbus Tags
OAS provides multiple ways to add and define tags:
- Manually add and define Tags using the Configure OAS application. …learn more…
- CSV Import and Export …learn more…
- Programatically …learn more…
- One Click Allen Bradley …learn more…
- One Click OPC …learn more…
To add a Tag manually:
- In the OAS Configure Application, select Configure >> Tags from the top menu.
- Select localhost or the remote service you wish to modify with the Select button to the right of the Network Node list.

- Click on the Add Tag button located at the top of the Tag browser on the left portion of the screen.

- A dialog box will appear. Enter a name for your new tag and click ok.
- A configuration screen will appear for your new tag. Select your data source type in in the Data Source dropdown box.
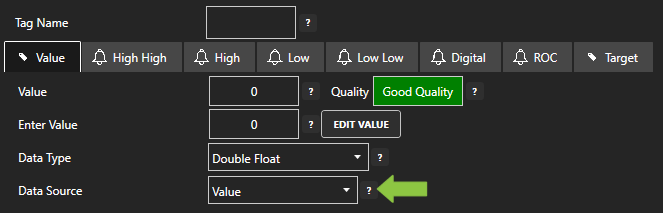
- Specify the correct data type in the Data Type dropdown box.
- Click Apply Changes at the bottom right of the window.
For more detailed instructions on configuring your tags, click here to see our Getting Started Tags tutorial.
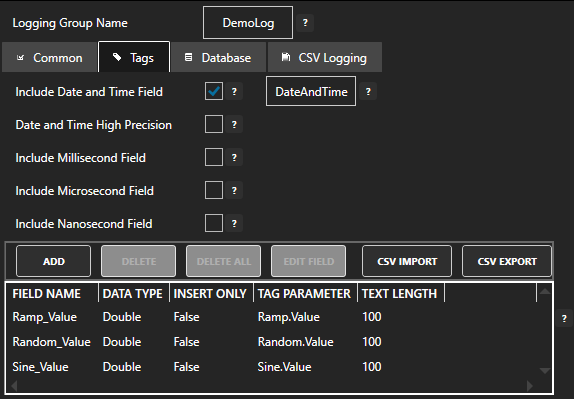
Step 4. Configure OPC Server Tags
OAS provides multiple ways to add and define tags:
- Manually add and define Tags using the Configure OAS application. …learn more…
- CSV Import and Export …learn more…
- Programatically …learn more…
- One Click Allen Bradley …learn more…
- One Click OPC …learn more…
To add a Tag manually:
- In the OAS Configure Application, select Configure >> Tags from the top menu.

- Select localhost or the remote service you wish to modify with the Select button to the right of the Network Node list.

- Click on the Add Tag button located at the top of the Tag browser on the left portion of the screen.

- A dialog box will appear. Enter a name for your new tag and click ok.
- A configuration screen will appear for your new tag. Select OPC in the Data Source dropdown box.

- Use the Browse button to the right of the OPC Item to browse OPC Servers for the desired OPC Item.
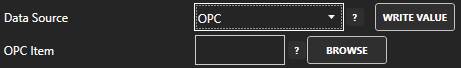
- Select Local, the desired OPC Server, branch within the OPC Server, and OPC Item and click OK.
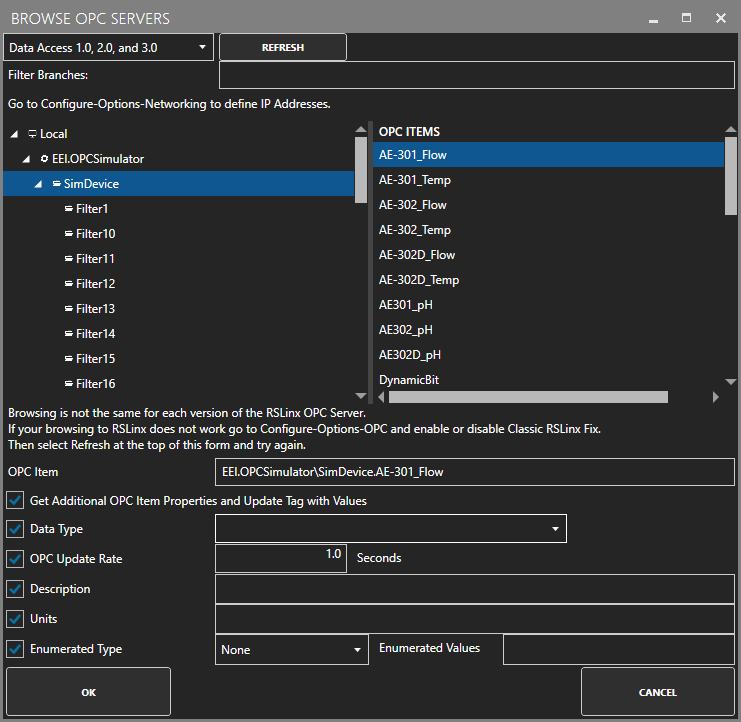
- Specify the desired OPC Update Rate for the Tag.
- Click Apply Changes at the bottom right of the window.
To add Tags with One Click OPC:
- In the OAS Configure Application, select Configure >> Tags from the top menu.

- Select localhost or the remote service you wish to modify with the Select button to the right of the Network Node list.

- To begin the One Click OPC process select the Group you would like to import to in the Tag configuration. If you want to import to the Root Level, select the Tags Group at the top of the tree.
Then select the One Click Import button on the top menu bar.

- Click on the Import OPC DA 2.XX or 3.0 Items Button in the pop up window.
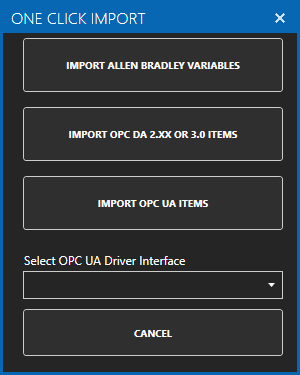
- Use the One Click OPC Wizard to browse for a branch as a starting position within an OPC Server or just select the OPC Server name itself to add all items from the selected OPC Server. For the best networking design select OPC Servers from Local even if you are configuring a remote OAS Service.
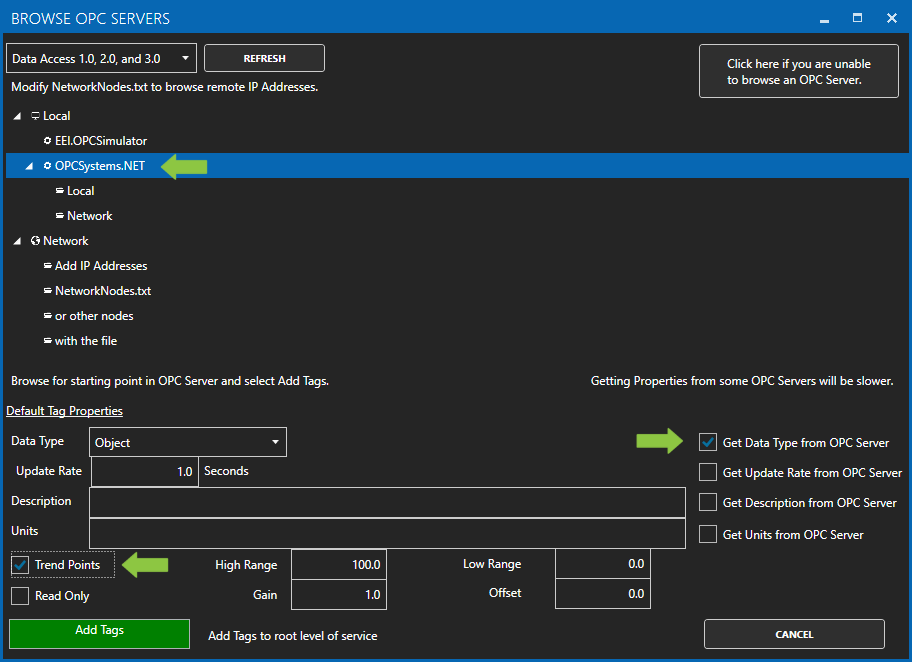
- Select to enable the options to Get Data Type from OPC Server and optionally the Descriptions. Additionally if you want to specify to Trend all of the points select Trend Points.
- Click Add Tags and it will automatically add all of the OPC Items from the OPC Server Branch you have selected and all of the sub Branches beneath it.
- Select the Save button on the toolbar at the top.
For more detailed instructions on Configuring OPC Server Tags, visit our Getting Started OPC tutorial or the One Click OPC tutorial or watch the video tutorial below:
Step 5. Configure the Target Tab of the Source Tags
- Select one of your source tags.
- Select it’s Target tab.
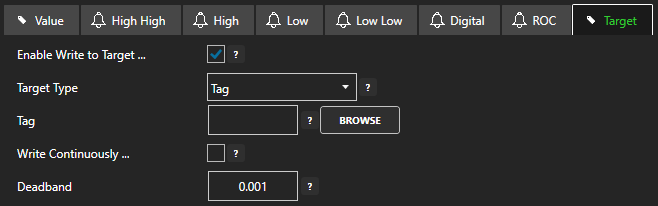
- Enable Write to Target
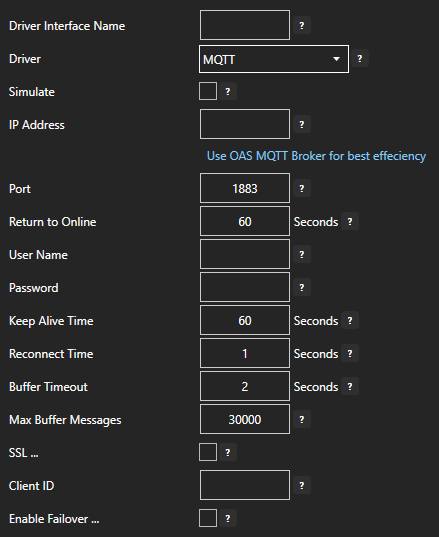
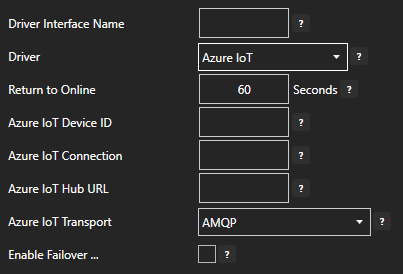
- Select the Target Type (Tag, OPC, Azure IoT, Azure IoT Edge, or MQTT) from the dropdown.
- Select the destination for the value to be sent.
If Tag is selected then select Browse and select the desired tag from the localhost system or optionally a remote system for transfer over a network.

Local: TagName.Value
Remote: \\192.168.0.1\TagName.Value
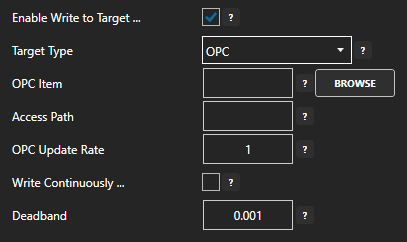
If OPC Item is selected select browse and select the OPC Server and Item
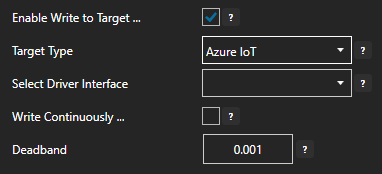
If Azure IoT is selected then select the Driver Interface.
If MQTT is selected then select the Driver Interface and Topic.
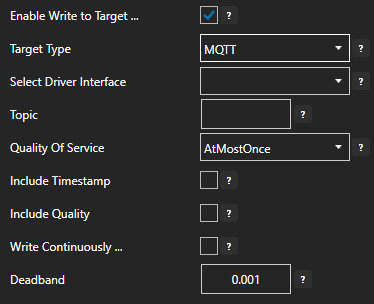
- Enter the desired float value Deadband field. Enter 0 for no deadband.
- If you want to specify a desired update frequency for the target check Write Continuously and enter the desired frequency. If Write Contentiously is unchecked the the target will be updated every time the source tag changes.
- Click the Apply Changes button to save your changes.
- Repeat this step for each tag that you want to transfer data from. This can also be done in bulk with CSV Import/Export or programatically.
For more detailed instructions on Configuring Data Route functionality, visit our Getting Started – Data Route tutorial or watch the videos below: