Videos – Networking
Networking
Edge network platform for IIoT communications. Host data directly at the source.
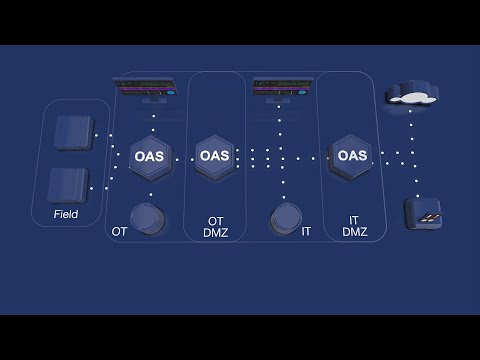
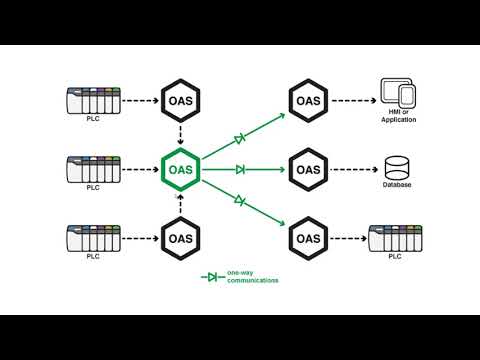
Typical OAS Deployment Architectures
The Open Automation Software is a flexible, configuration based data platform with a virtually unlimited number of possible use cases and solution implementations. OAS can operate across network boundaries and between private and public networks.
Edge Networking
Edge networking for hosting live data values with store-and-forward and accurate status.
- Basic Networking
- Live Data Cloud proxy
- Unidirectional Networking
Basic Networking
How to network all products to central service using a fixed IP Address or registered domain name for the Internet.
Unidirectional Gateway
How to transfer data through networks with one way communication data diodes.
Live Data Cloud
How to host data from any Windows PC with a standard Internet connection. No fixed IP Address or registered domain name required.
Adjustable WCF Port Number
How to adjust WCF port number in the realtime service and all client applications.
Modern OAS now uses TCP Port Number with default value of 58727 which is also adjustable with the same methods.
Excel with Live Data Cloud
How to use OPCExcel.NET with data service being hosted with free Live Data Cloud feature over the Internet.
Data Log with Live Data Cloud
How to use Data Logging with data service being hosted with free Live Data Cloud feature over the Internet.
OPC Client with Live Data Cloud
How to use OPCClient.NET with data service being hosted with free Live Data Cloud feature over the Internet.
Set Default Network Adapter for Driver Interfaces
If the communications for the Modbus, Allen Bradley, or Siemens driver is not working at all you may need to set the default network adapter priority in the operating system. Use the following steps to set the network priority.
Step 1
Click Start and in the search field type View network connections.
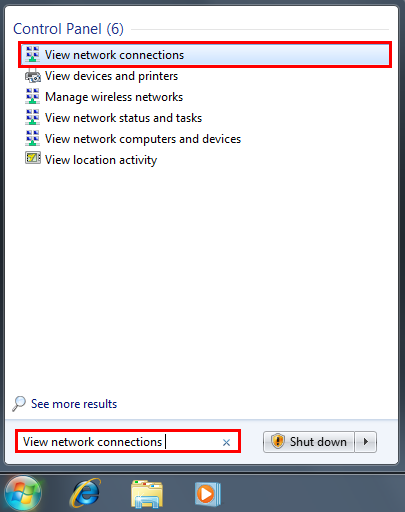
Step 2
Press the ALT key, click Advanced Options and then click Advanced Settings.
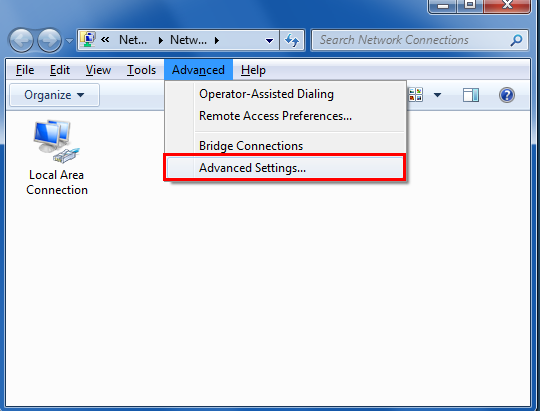
Step 3
Select Local Area Connection and click the green arrows to give priority to the desired connection.
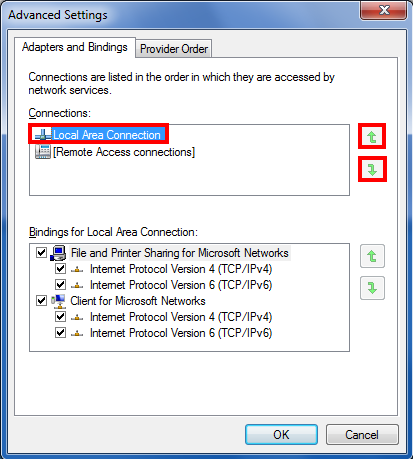
Step 4
After organizing the network connections available according to your preferences, click OK.
The computer will now follow an order of priority when detecting available connections.
Getting Started – Networking
Networking functionality is a core feature of Open Automation Software and is also known as the Distributed Network Architecture (DNA) feature. As outlined in the Networking Overview, there are three main communication types that OAS provides for transferring tag data between OAS Engines and clients depending on what networking architecture is required:
These methods can be used in isolation or together to achieve different types of networking architectures and allow you to move you data from your data sources to your data destinations.
Within the context of OAS Networking discussed here, a client could be defined as another OAS Engine or one of the OAS .NET connectors or .NET HMI or Web HMI components used for reading and writing tag data. Whilst features such as the REST API, MQTT and Cloud based connectors are also used to transfer tag data, these are not considered core features of OAS but rather considered separate drivers with independent configuration options.
When is Networking used?
The Networking functionality of OAS is used whenever you move data between two or more OAS Engines or between an OAS Engine and one or more OAS clients. More specifically, when we are talking about data, we are actually talking about Tag data. A Tag is the fundamental representation of a unit of data in OAS and consists of a value, a timestamp and a quality state. The tags you define and organize in OAS represent your data model – be it a business process, a monitoring processes or some other logical representation of a physical state.
Using the configurable features of OAS, you can move tag data between engines and between engines and clients without having to do the heavy lifting of implementing any communications protocols yourself. Your own custom solutions and applications can leverage existing OAS libraries to read and write data – all you need to know is the tag path, name and parameter name you wish to read or write. The power of OAS Networking becomes more apparent with an understanding of Remote Tag Access.
When a tag is referenced locally to a particular OAS Engine (for example, by setting a tag’s data source to Tag and pointing to another tag) or from a client connected to a particular instance, it can be simply referenced by the path, name and parameter, as mentioned previously. This looks something like this:
MyTag.ValueLet’s now look at how you might reference a tag on a remote OAS Engine. In other words, an OAS Engine or client referencing a tag that is not on the same OAS Engine or the OAS Engine that the client is connected to. This is where the Basic Networking communication comes in. When you want to reference a tag on a different OAS Engine it is as easy as adding the remote node’s IP address, host name or domain name.
\\Instance1\MyTag.ValueOAS will handle all of the engine to engine data transfer automatically and you do not need to do anything differently in your clients. In the diagram above, you can see that the client is connected to Instance2, but the tag reference is a remote tag reference. Instance2 will automatically route the request to Instance1 and retrieve the data. Depending on if you are using a .NET or a Web client (see next section) the remote tag access will be configured slightly differently.
👉 More information about Basic Networking 🔗
The second remote tag access method is the Live Data Cloud method. This is where tag data is routed through an intermediate OAS Engine and is designed to allow separation of networks. In this type of communication, tags are referenced using the alias name of the Live Data Cloud host node. For example:
\\www.opcsystems.com\RemoteSCADAHosting.Instance1.MyTag.ValueIn this case the domain www.opcsystems.com represents the Live Data Cloud host node and Instance1 is the alias for one of your internal OAS Engine instances. The RemoteSCADAHosting prefix let’s OAS know that this special format is being used. The remainder of the tag path is the same as a standard tag reference.
👉 More information about Live Data Cloud 🔗
.NET vs Web Clients
Clients within the context of OAS can be divided into two general categories – .NET clients and web clients.
.NET clients include the OAS Configuration Tool and any custom application that uses the .NET OAS components such as:
These components will natively communicate with an OAS Engine using the core TCP networking functionality provided by OAS as explained in the Networking Overview.
The web clients on the other hand use HTTP based protocols to communicate with the OAS Engine. These components include:
Licensing
Networking functionality is enabled with the DNA feature enabled in your license. You can check your license in the OAS Configuration tool by going to the Configure > License screen and checking that you can see the phrase Networking is Enabled.
There are some architectures that do not require networking, such as hosting services on one server
The Live Data Cloud hosting server does not need a license as its only purpose is to route traffic between data source servers and clients. Your OAS Engine at the data source will typically be licensed for the features and drivers that you require.
Configuration
For OAS Engine configuration changes you have the option to use the OAS Configuration tool or to use the .NET OAS Configuration SDK or the Server Configuration REST API. From this point on this guide will only mention the OAS Configuration tool in order to minimize duplication.
Limits
➡️ Each OAS Engine can support up to 10,000 simultaneous client connections.
➡️ Each client application can support connections with up to 10,000 independent OAS Engines.
➡️ The resources of your hosting server or environment as well as the networking bandwidth and connection quality may play a role in the overall performance of the system. It is important to monitor the CPU, memory, storage and network throughput of your environment to ensure OAS is performing as expected.
Polling Rate
Clients will request tag data from an OAS Engine at a regular interval. The first poll will send all requested tag data and any subsequent poll will only send data changes.
The default polling rate for clients is 30 milliseconds. This can be configured using the OAS Configuration tool on the Networking tab of the Configure > Options screen.

Recommended polling intervals for larger number of client connections:
- > 100 client connections — 100ms
- > 1,000 client connections — 1,000ms
⚠️ The OAS Engine will need to be restarted for the change to take effect.
Listening Ports
OAS uses a number of standard ports for communication between OAS Engines and clients depending on the technology that is used.
OAS Engine and .NET client OAS components
For OAS Engine to OAS Engine and for OAS Engine to non-web client OAS component communications two ports are exposed on the OAS Engine. These are called the primary and backup ports. These ports provide a bidirectional, compressed and encrypted data stream.
- Port 58727 – Primary Port Number
- Port 58737 – Backup Port Number
The backup port is used to listen for incoming client connections should there be a problem with the primary port. The OAS Engine will automatically attempt to use the backup port if the primary port is not available. The following diagram illustrates OAS Engine to OAS Engine communications.
The following diagram illustrates OAS Engine to non-web clients where the OAS Dotnet libraries are used for OAS Engine communications. This allows OAS components and HMIs to use the same benefits of compression and encryption. Note that all of the non-web clients will use the primary port, except the OAS Configuration Tool which will use the backup port if the primary port is not available.
Web clients
Web based clients and REST API clients use a different port to the primary and backup port exposed by the OAS Engine. This is because the web-based components do not use the same TCP stream based data transfer, but instead require a HTTP style communication API.
- Port 58725 – Web and REST API Port Number
The Web API port is used for web-based clients such as the Web HMI JavaScript based features and controls. It is also used by the REST API and UIEngine.
Legacy Ports
There are two legacy port numbers used for communicating with old versions of OAS using the WCF or the .NET Remoting frameworks.
- Port 58724 – Legacy WCF Port Number for OAS version 11 or older
- Port 58723 – Legacy .NET Remoting Port Number for OAS version 4 or older
These port numbers are not configurable and are not available on Linux. To enable communication with a legacy OAS version using .NET Remoting, you can enable this feature by ticking the Enable Classic TCP (Unsecure) checkbox.
Port Configuration
The primary, backup and web ports listed in previous sections are configurable using the OAS Configuration tool on the Networking tab of the Configure > Options screen. Note that if you make changes to these ports there may be other applications that need to be updated. For example, the OAS Configuration tool and the OAS Service manager application will need to use the updated primary port to function correctly. Similarly, any OAS Engines or clients will need to be updated – for more details see the Change Network Port Numbers page.
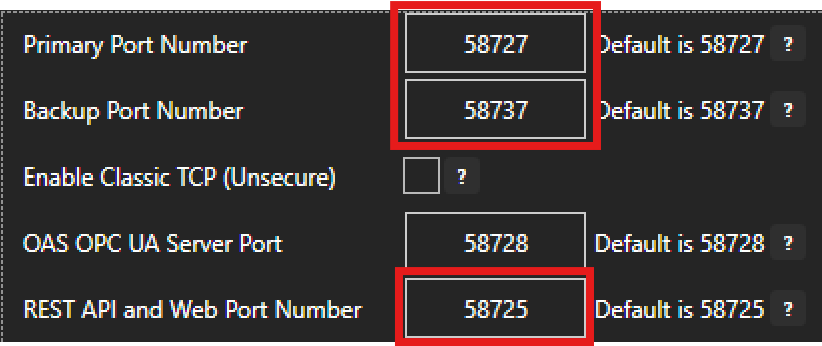
Remote Services Ports
An OAS Engine (local engine) can communicate with a remote OAS Engine (remote engine) using the default port configurations as listed in the previous section. However, if you choose to change the listening ports on the remote engine and the local engine needs to communicate with the remote engine, then you will need to configure the Client Ports on the local engine to match the ports used by the remote engine.
You can configure the client port settings in the OAS Configuration tool on the Remote Services tab of the Configure > Options screen.
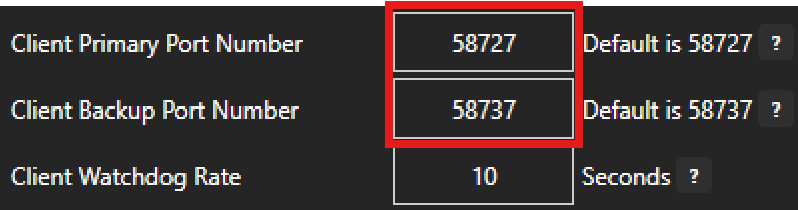
⚠️ Note that this setting will apply to all client communication initiated by the local engine. In other words, all remote engines that the local engine needs to connect to must have the same primary port numbers and the same backup port numbers. You cannot have a local engine that connects to two different primary port numbers or two different backup port numbers.
The Client Watchdog Rate parameter allows you to set a communication retry timeout on the local engine. If no communication is detected for the given number of seconds, the connection will be reset and a new reconnection attempt will be made.
Security
Access to reading and writing tag values is managed using OAS Security features. This includes creating user accounts with specific permissions that OAS Engines and clients will use to authenticate as well as mechanisms to manage permissions for reading and writing at the tag level.
👉 More information about Security 🔗
👉 More information about Restricting Tag Access 🔗
Networking

Overview – Networking
All features of Open Automation Software including configuration tools and all .NET components support remote connections over your LAN, WAN, VPN, and the Internet. Visit the OAS IoT Network page for comparison of advantages over typical cloud networks which are push/pull communications.
There are 4 networking features that can be used individually or combined together to support communications through corporate firewalls, access to systems without a fixed IP address, and through one way communication diodes.
Basic Networking with Static IP Address
Live Data Cloud Networking with Dynamic IP Address at Data Source
Network Forwarding for redirect path through any number of servers
One Way Networking for transferring through communication diodes
Visit each networking page for syntax examples on how to define client access to remote data services.
Visit the Getting Started-Networking page for helpful features like network node aliasing in client applications and how to check if your TCP port is open.
All communications for Open Automation Software uses WCF communications with an encrypted and compressed byte stream. The data that is transported from clients to services only transfers the data that each client has requested.
Once all of the values are transferred only data points with new values are transmitted in the next packet. So if no new data occurs in the service the packet to the requesting client will contain 0 values. The default rate at which clients will try to obtain data from the service is 100 ms. This can be made faster or slower by setting the property Client Packet Rate under Configure-Options of the service.
Every client that is communicating with the service will obtain this value when communications is first established. If a client cannot get a return back from the service within 5 seconds the connection will be considered lost. The Client Watchdog rate can be set for each client. Both the service and the client will know when the connection is lost and data.
The actual amount of network traffic that is used is at the smallest possible packet size with WCF communications to be able to transfer the value, timestamp, and quality for each tag value to each client.
If you have several remote clients need the same data from a remote service a second service can be setup with remote Tags as a data source to the first service, and all of the clients can communicate to the second service. This would be for all read only data to reduce the communications from a data source service from a remote location with low bandwidth. For any points that need to be written this can be done directly from each client to the remote service.
More:
- Basic Networking
- FAQs - Networking
- FAQs - UDP Broadcast
- Frequently Asked Questions - Live Data Cloud
- Getting Started - Networking
- Getting Started - Unidirectional Network Gateway
- Live Data Cloud Networking
- Network Forwarding
- Networking Ports
- One Way Networking
- Remote OAS Service Access
- Troubleshooting - Networking
- Videos - Networking
- Videos - UDP Broadcast
- WINNAT Blocking Port
Frequently Asked Questions – OPC Client
Please enable .NET Framework 3.5 in the operating system and then reinstall OAS.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/framework/install/dotnet-35-windows-10
Step 1 – Unregister server.
Using the Windows Command Prompt running As Administrator go to the directory C:\Program Files\Open Automation Software\OAS\ and type DANSrv.exe /Unregserver.
Step 2 – Register to run as a Windows Service
Using the Windows Command Prompt running As Administrator go to the directory C:\Program Files\Open Automation Software\OAS\ and type DANSrv.exe /Service /AutoStart.
Step 3 – Verify OPC Server is Registered
Using the Service Control Manager the Windows Service OPCSystems.NET DA Server should be listed to run in Automatic Startup Type. You can select to manually start the server or restart the operating system and the server will start automatically.
<add key=""ValueOnlyBrowsing"" value=""False""/>
<add key=""TCPPortNumber"" value=""58727""/> <add key=""WCFPortNumber"" value=""58724""/>View the following video on how to adjust WCF port number in the realtime service and all client applications:
Note: Remoting is a legacy format of communications and it is recommended to update to the latest version of OAS for the most secure transport.
For the OPCSystem.NET OPC Server modify the file DANSrv.exe.config in the directory C:\Program Files\Open Automation Software\OAS] with Notepad or a text editor.
Set the property EnableRemoting to True.
<add key=""EnableRemoting"" value=""True""/>
<add key=""UserName"" value=""""/> <add key=""Password"" value=""""/>
Videos – OPC Client
OPC Client Connector
Connect third party OPC Clients to OPC Servers over the Internet and through your WAN. Enable OAS as a data source to third party SCADA software.
OPC Clients
How to connect third party OPC Clients for both local and Internet connections.
OPC Client with Live Data Cloud
How to use OPCClient.NET with data service being hosted with free Live Data Cloud feature over the Internet.
OPC Client Connector Runtime
There are over 800 variable types for each Tag. Of each of these you will alarm limits, alarm status, Time On and Count values, Total, and more.
Following are the most commonly used parameters:
- Value is the actual value of the Tag and can have Read and Write access if the Tag Source is set to Value or OPC Item. Read only if the Source is set to Calculation or remote Tag. The data type depends on the Tag’s Data Type.
- HighHighAlarmLimit is the High High Alarm Limit of the Tag and can have Read and Write access if the Tag Source is set to Value or OPC Item. Read only if the Source is set to Calculation or remote Tag. The data type is a Double or VT_R8.
- HighAlarmLimit is the High Alarm Limit of the Tag and can have Read and Write access if the Tag Source is set to Value or OPC Item. Read only if the Source is set to Calculation or remote Tag. The data type is a Double or VT_R8.
- LowAlarmLimit is the Low Alarm Limit of the Tag and can have Read and Write access if the Tag Source is set to Value or OPC Item. Read only if the Source is set to Calculation or remote Tag. The data type is a Double or VT_R8.
- LowLowAlarmLimit is the Low Low Alarm Limit of the Tag and can have Read and Write access if the Tag Source is set to Value or OPC Item. Read only if the Source is set to Calculation or remote Tag. The data type is a Double or VT_R8.
- DigitalAlarmLimit is the Digital Alarm Limit of the Tag and can have Read and Write access if the Tag Source is set to Value or OPC Item. Read only if the Source is set to Calculation or remote Tag. The data type is a Boolean or VT_BOOL.
- AlarmStatusHighHigh is a read only Boolean indicating the current state of the Tag’s High High alarm condition.
- AlarmStatusHigh is a read only Boolean indicating the current state of the Tag’s High alarm condition.
- AlarmStatusLow is a read only Boolean indicating the current state of the Tag’s Low alarm condition.
- AlarmStatusLowLow is a read only Boolean indicating the current state of the Tag’s Low Low alarm condition.
- AlarmStatusDigital is a read only Boolean indicating the current state of the Tag’s Digital alarm condition.
OPC Client Connector Using IP Address
You can use an IP Address to define a remote Open Automation Software Tag instead of a Network Node name.
If the OPCSystems.NET OPC Server is on the same computer as an OAS Engine use the Configure OAS application to select Configure-Options-Networking and add the IP address of the remote PC you want to list.
If you have only installed the OPCSystems.NET OPC server on the OPC client system modify the NetworkNodes.txt file that is located in the installation directory of the OPCSystems.NET OPC Server. The default installation directory is C:\Program Files\Open Automation Software\OAS\.
OPC Client Connector Browsing
The registered name of the OPC Systems.NET OPC Server is OPCSystems.NET.
There are two (2) basic root branches to browse to:
- Local. To browse to all Tags on the Local node select the Local branch.
- Network. To browse to remote network nodes select the Network branch.
![]()
When browsing through a Network branch other branches appear with the Network Node name of all systems on your network. You can only successfully browse nodes that have the Open Automation Software Service running with a Tag configuration loaded.
Browsing Local or Network node you will be able to all groups and sub groups in the Tag configuration as branches.
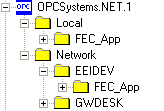
When you select a group or base Service node you will be able to see all Tag Parameters for that branch as Items.
You can also use DirectOPC interface to browse directly to OPC Servers bypassing the Open Automation Software Tags.
Note: There are multiple Parameter types for each Tag. By default only Value parameters will appear for browsing for effiency and performance. If you prefer to browse all parameters of a tag modify the file C:\Program Files\Open Automation Software\OAS\DANSrv.exe.config and change the following to False.
– Only shows Values of a Tag.
– Shows all parameters and properties of a Tag.
Parameter types
There are over 800 variable types for each Tag. Following are a few of the most common variables.
- Value is the actual value of the Tag and can have Read and Write access if the Tag Source is set to Value or OPC Item. Read only if the Source is set to Calculation or remote Tag. The data type depends on the Tag’s Data Type.
- HighHighAlarmLimit is the High High Alarm Limit of the Tag and can have Read and Write access if the Tag Source is set to Value or OPC Item. Read only if the Source is set to Calculation or remote Tag. The data type is a Double or VT_R8.
- HighAlarmLimit is the High Alarm Limit of the Tag and can have Read and Write access if the Tag Source is set to Value or OPC Item. Read only if the Source is set to Calculation or remote Tag. The data type is a Double or VT_R8.
- LowAlarmLimit is the Low Alarm Limit of the Tag and can have Read and Write access if the Tag Source is set to Value or OPC Item. Read only if the Source is set to Calculation or remote Tag. The data type is a Double or VT_R8.
- LowLowAlarmLimit is the Low Low Alarm Limit of the Tag and can have Read and Write access if the Tag Source is set to Value or OPC Item. Read only if the Source is set to Calculation or remote Tag. The data type is a Double or VT_R8.
- DigitalAlarmLimit is the Digital Alarm Limit of the Tag and can have Read and Write access if the Tag Source is set to Value or OPC Item. Read only if the Source is set to Calculation or remote Tag. The data type is a Boolean or VT_BOOL.
- AlarmStatusHighHigh is a read only Boolean indicating the current state of the Tag’s High High alarm condition.
- AlarmStatusHigh is a read only Boolean indicating the current state of the Tag’s High alarm condition.
- AlarmStatusLow is a read only Boolean indicating the current state of the Tag’s Low alarm condition.
- AlarmStatusLowLow is a read only Boolean indicating the current state of the Tag’s Low Low alarm condition.
- AlarmStatusDigital is a read only Boolean indicating the current state of the Tag’s Digital alarm condition.
A typical full OPC Item with a Tag defined directly under the Service root for Tag on the local OAS Service is Local.Ramp.Value.
A typical full OPC Item with a Tag defined directly under the Service root for Tag on a remote OAS Service is Network.NetworkNode.Ramp.Value or Network.192.168.1.0.Ramp.Value. Either will resolve to enable network communications with the remote Open Automation Software Service and can also be used for the local Open Automation Software Service if the local NetworkNode or IP address is the local system.