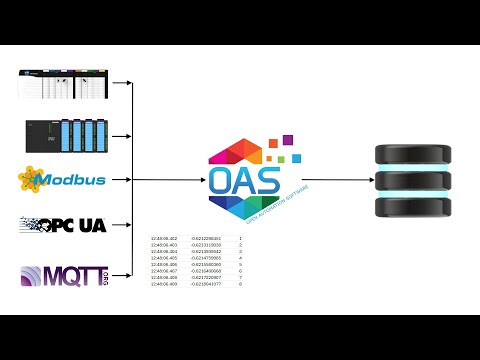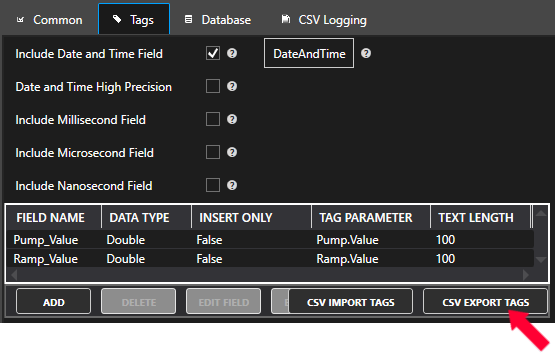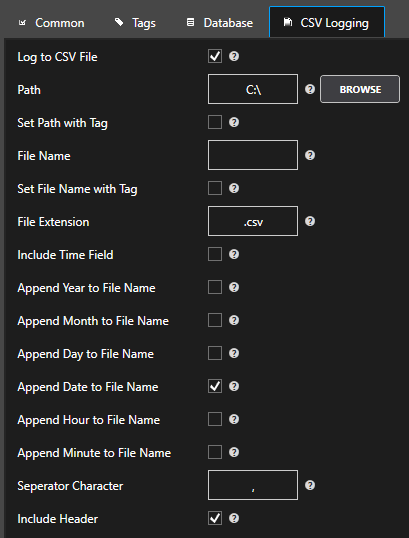
Log To Database
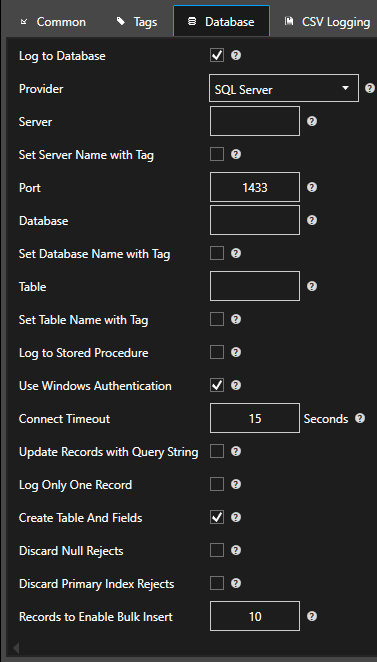
Enable Logging to a database table. Logging Active must also be set to True.
Provider
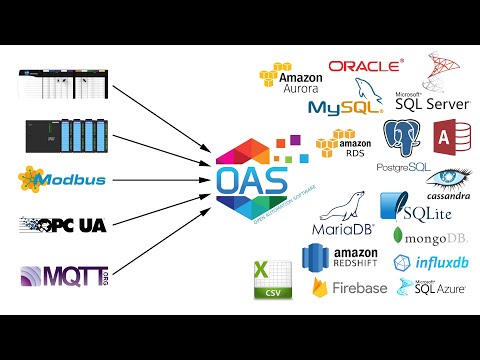
Database provider to use:
- SQLServerDesktop_MSDE: Use SQL Server Desktop or MSDE database engine.
- SQLServer: Use SQL Server or SQL Server Express.
- MSAccess: Use Microsoft Access Jet Database engine.
- Oracle: Use Oracle engine. Does not automatically create database. You must create the database schema first to use this provider.
- mySQL: Use mySQL database engine.
- ODBC: Use ODBC data source. Does not automatically create database, table, or field names. You must create database, table, and all fields with the proper names and data types first to use this provider.
- MongoDB: Use MondgoDB NoSQL engine.
Server
The name of the Server to use when the Provider (see above) is set to SQL Server Desktop, SQL Server, or mySQL.
Set Server Name with Tag
When enabled the server (see above) name can be dynamically set with a Tag Parameter value when the Provider is set to SQL Server Desktop, SQL Server, or mySQL.
Database
The name of the Database to log to. When using Microsoft Access specify the full path of the database. Example: C:DatabaseName.mdb.
Set Database Name with Tag
When enabled the database name can be dynamically set with a Tag Parameter value.
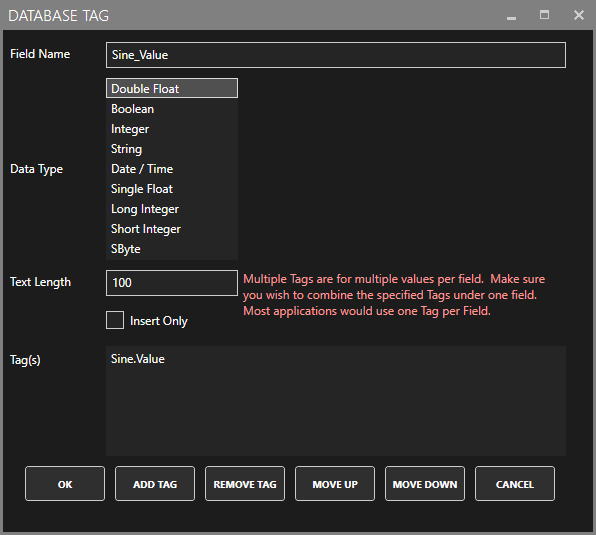
Table
The name of the database Table to log to.
Set Table Name with Tag
When enabled the table (see above) name can be dynamically set with a Tag Parameter value.
Log To Stored Procedure
Log values to stored procedure instead of a table.
Stored procedure must already exist.
Table name property will change to Stored Procedure name.
Database field names will be the stored procedure parameter names.
Use WinNT Authentication
Use Windows Logon Security Authentication when the provider is set to SQL Server Desktop or SQL Server.
User Name
User Name for database security.
Password
Password for database security.
Update Records with Query String
This will enable an update to the table instead of an insert. The records that match the Query String will all be updated. If no records are found to match the Query String then the record can be inserted if the option Insert if Records Do Not Exist from Query String (see below) is enabled.
Data Logging Query String
The query string to use to find matching records to update when the option Update Records with Query String is enabled.
Set Query String with Tag
When enabled the Query String (see above) will be dynamically set based on the value form a String Tag.
Insert if Records Do Not Exist from Query String
If the option Update Records with Query String is selected and the Query String value does not result in any matching records a new record will be added to the table if this option is selected.
Log Only One Record
When enabled and the Logging Type is set to Continuous, Even Driven, Specific Time of Day, or Data Change Row all of the records in the table will be deleted except the latest one in the table.
When enabled and the Logging Type is set to Data Change the existing records that have the matching tag alias name will be updated. If there are no matching records that exist then a new record will be added.
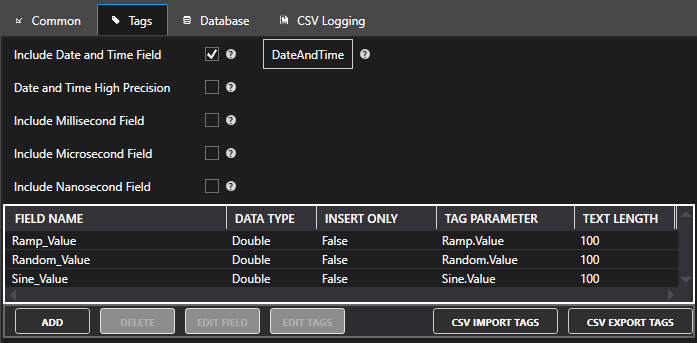
Automatically Create Table And Fields
If the table does not exist it will automatically be created with the fields defined under the Tags properties
If the table does exist each field will be verified to match data type and field name. Fields that do not exist in the table will be created. Fields that do exist and their data type does not match the data type defined will be converted to the defined data type.
When this option is disabled no attempt will be made to create the table or fields and the table must already exist with the correct field names and types.
Do Not Buffer When Nulls Are Not Allowed In Database
When this option is selected and one or more of the fields has been changed to not allow nulls and the data quality of the value is bad an error will occur in the logging that nulls are not allow. With this option selected the record will be ignored and will not be buffered for the field to be corrected, the record will be lost.
Do Not Buffer On Primary Index Failure
When this option is selected and an error indicating that the PRIMARY INDEX violation has occurred data will not be buffered to RAM or disk. With this option selected the record will be ignored and will not be buffered and the record will be lost.
Number of Records to Enable Multiple Write
The number of records to be logged that will cause the logging to use an optimized logging of multiple records in one call when using the SQL Server provider.
Try Single Write After Multiple Write Fail
When using SQL Server and the number of records to be logged exceed Number of Records to Enable Multiple Write (see above) and the optimized write fails try an individual stored procedure write.
Multiple Write With TableLock
When using SQL Server and the number of records to be logged exceed Number of Records to Enable Multiple Write the optimized write will be called with a TableLock.
Use Get App Lock
When using SQL Server and the number of records to be logged exceed Number of Records to Enable Multiple Write only one call at a time will be able to processed for all logging groups that have Use Get App Lock enabled. This will disable parallel processing to the database to only execute one data logging group to the database at a time when using SQL Server. Does not apply to Oracle, Access, and mySQL.
Fire Events on Multiple Write
When using SQL Server and the number of records to be logged exceed Number of Records to Enable Multiple Write the optimized write will fire an event on each execution.
Number of Records to Write on Multiple Write
When using SQL Server and the number of records to be logged exceed Number of Records to Enable Multiple Write the optimized write will include this number of records in each batch write. This is a way to break up the network packet size to remote SQL Server nodes with large amounts of data to record. A value of 0 will write all records in one batch.