The Data Route feature represents one of the most powerful features of the Open Automation Software Platform. Its effectiveness as an industrial automation solution is derived in large part from its great flexibility, as it has a variety of different use cases.
However, prior to discussing specific capabilities and uses it is important to have a sound understanding of what the Data Route feature is fundamentally.
To those readers well versed in the space of industrial automation the term ‘data route’ is most likely familiar and intuitive. To those newer to the world of industrial automation, Data Route is essentially a protocol translation service that allows communication between disparate devices/controllers.
The world of programmable logic controllers and machine-to-machine communications is chock full of proprietary protocols and many enterprises will use controllers from more than just one vendor. The ability to communicate across these proprietary barriers represents a boon to engineers and operations managers who can now consolidate various data and simplify network communications across their entire enterprise.
Tag-to-Tag Transfer
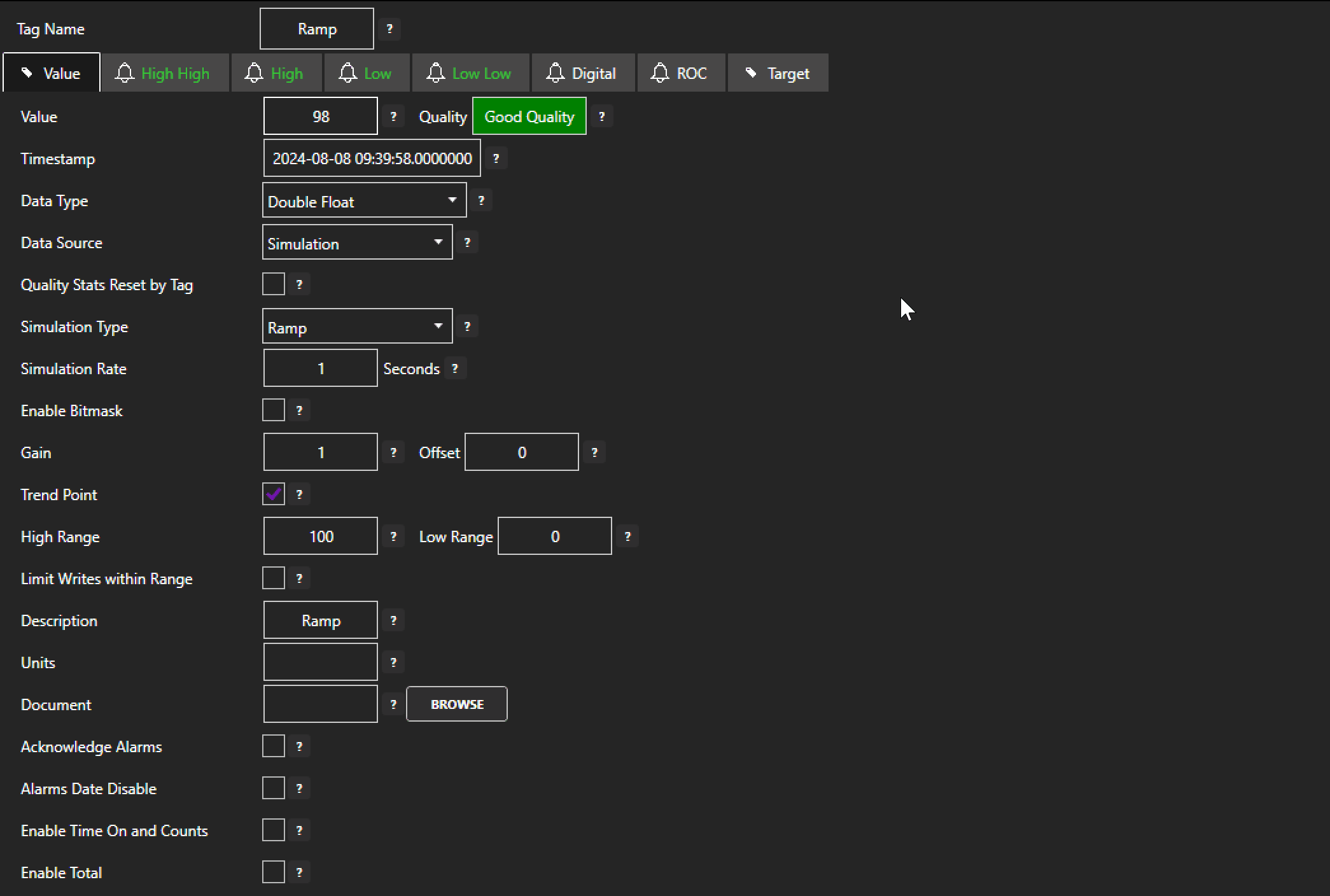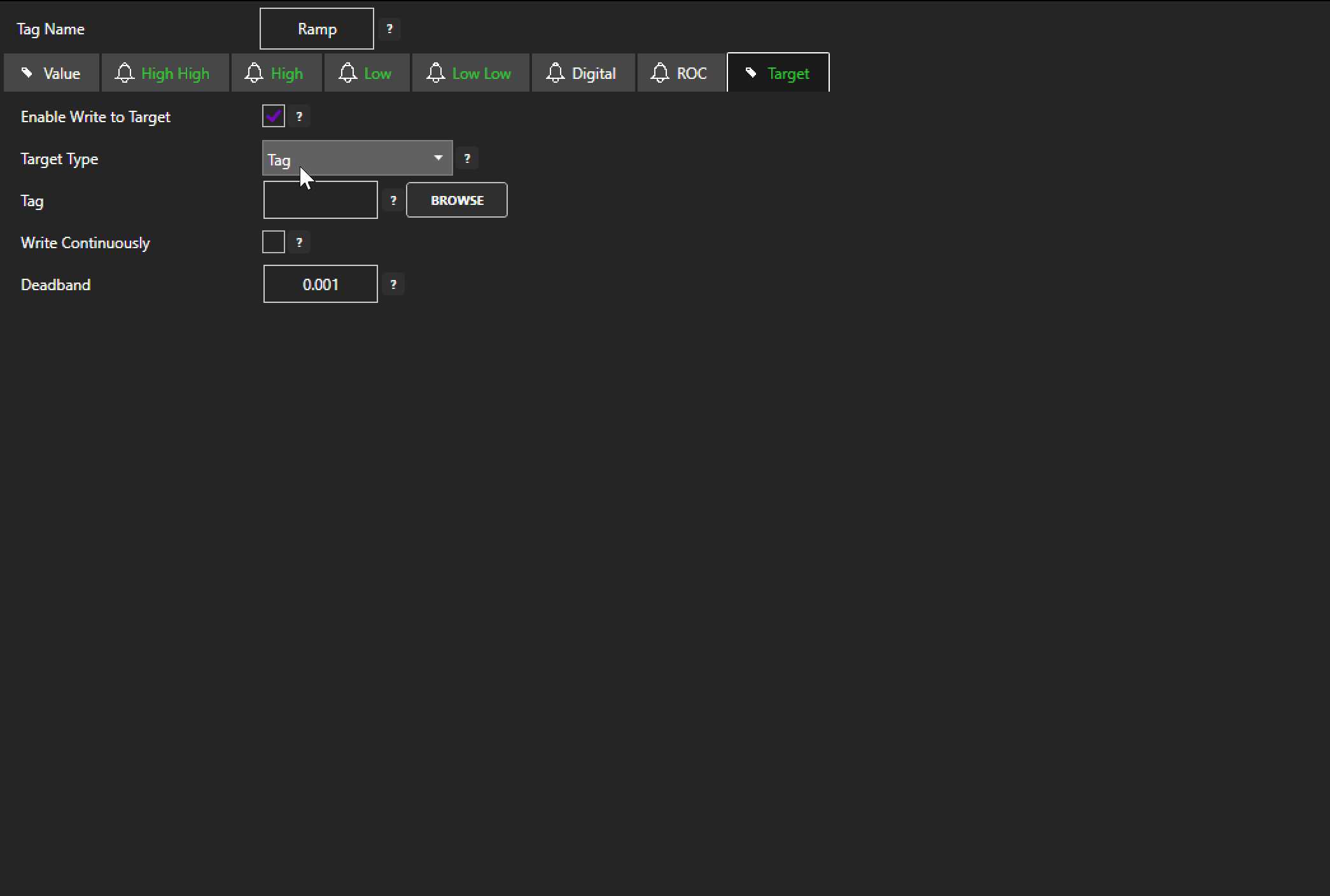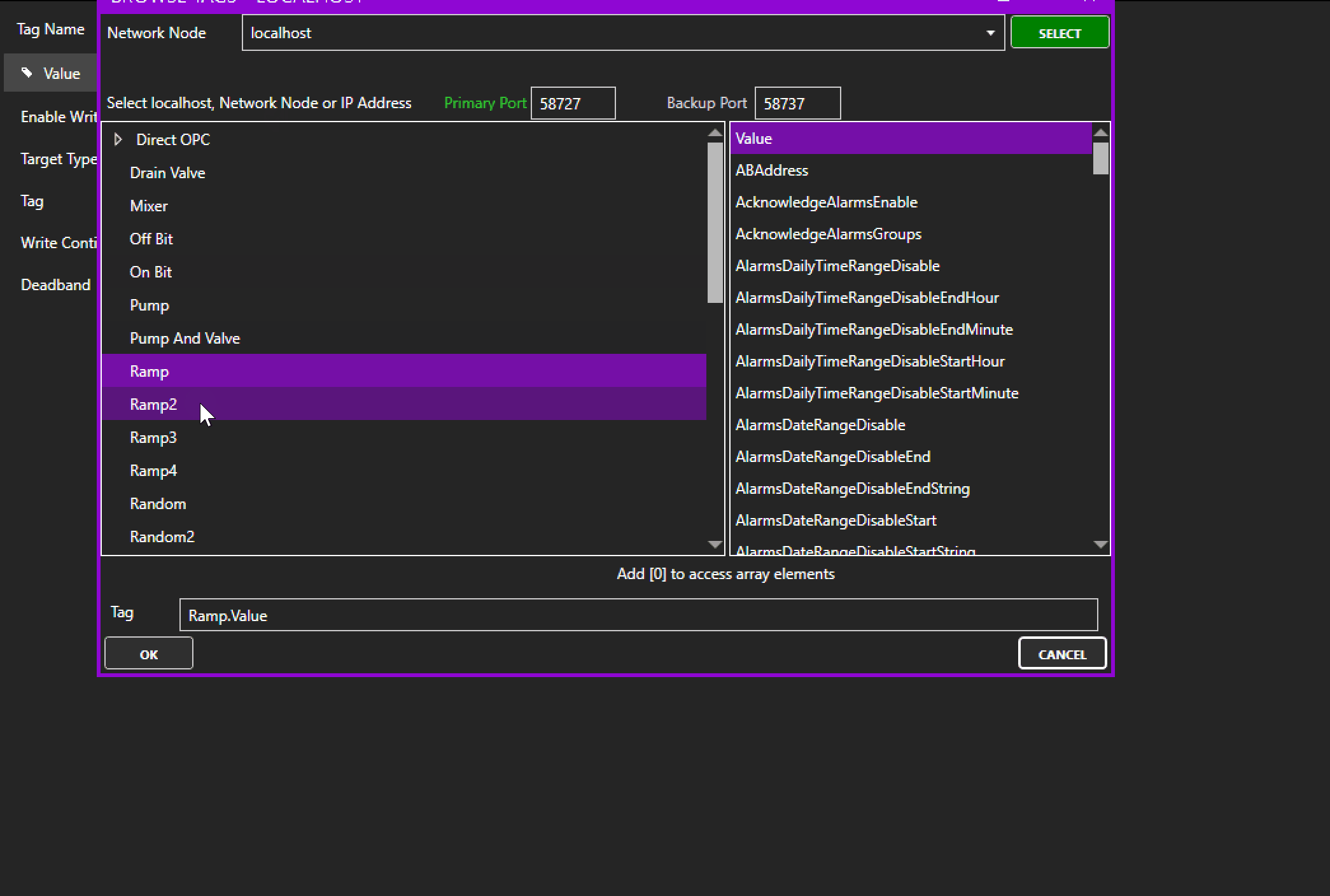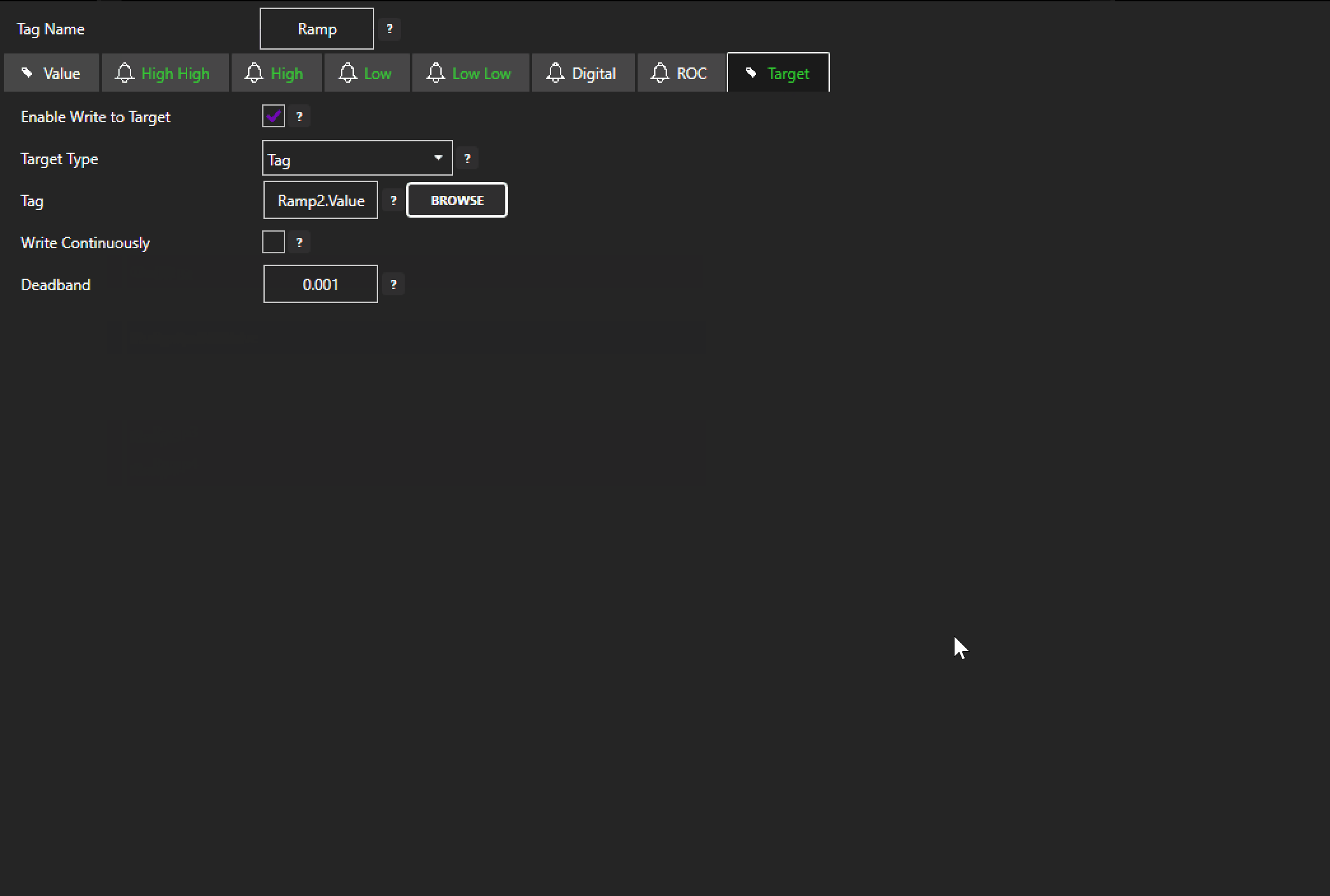
The first method comes built-in to the OAS Tag Configurator module and does not require the configuration of a distinct Data Route group. Although, it does still require that Data Route be an enabled feature on the OAS license.
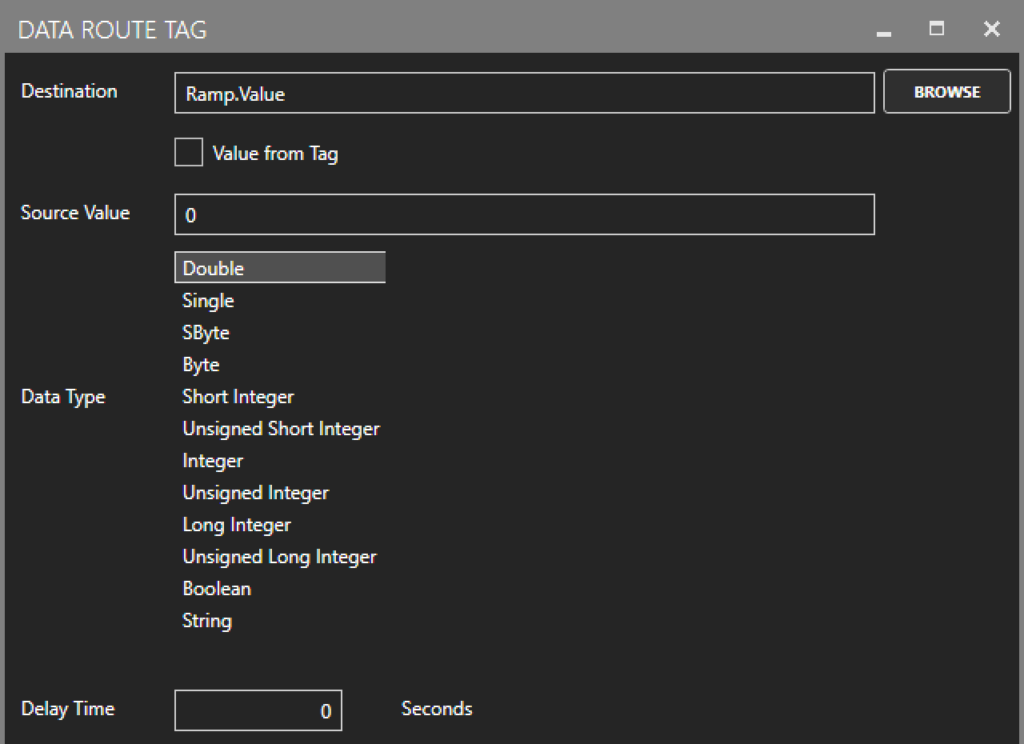
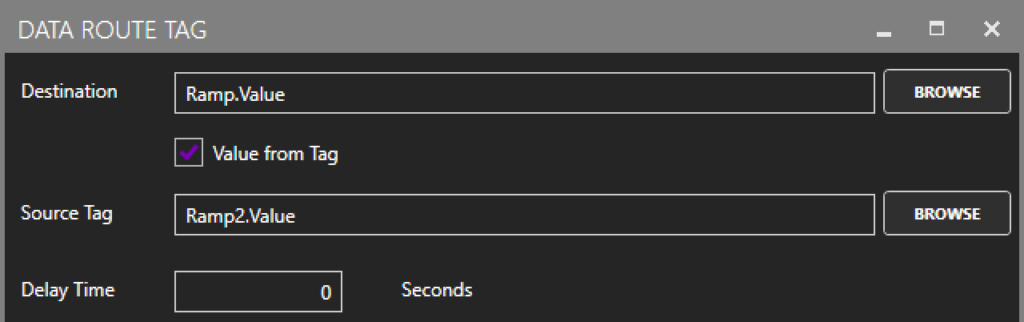
Each configured Tag comes with an option to activate ‘Enable Write to Target’. Activating this option instantly presents the users with the option to write the value of what will now be referred to as the ‘source tag’ to any other tag (the destination tag) of the user’s choice. By default, Data Route will write the source tag’s value to the destination tag any time the value of the source tag changes, but the user also has the option to write continuously at a user specified frequency. Learn more on the details of this feature here.
And just like that, what would have been a few days or weeks of writing custom code or configuring protocol communications is reduced to less than 60 seconds. This lightweight routing capability built directly into the Tag Configurator is great for setting up the transfer of a handful of critical data points between your devices. Although for larger scale routing and finer control, users will want to configure a proper Data Route group to transfer multiple tags at once.
Multiple Tag Transfer
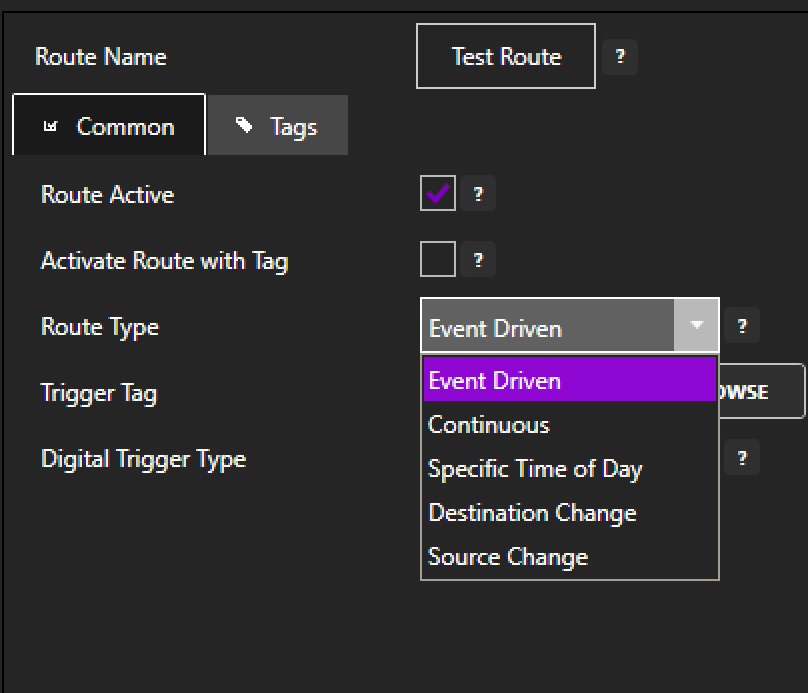
While the simple Tag-to-Tag transfer option available for each individual tag is convenient, it may not give users the level of control and scale desired. Configuring a proper Data Route group is where the full power of the Data Route feature comes to bear. Users can add as many tags to a Data Route group as desired and write data to multiple tags simultaneously or independently based on a wide array of conditions.
Users can easily browse for desired destination tags to add to a group and on a tag-by-tag basis, configure Data Route to write either static values or dynamic values from other (‘source’) tags. Some Data Route groups could potentially contain many tags which is why OAS has built-in CSV export/import functionality. This makes for simple manipulation of large groups of tags.
Creating a formal Data Route group also grants the user additional options with regards to how/when the data is transferred. Like the ‘Enable Write to Tag’ feature, data write can be triggered any time the value of a given source tag changes – ensuring any changes in data can be quickly communicated to any other device needing the data – or be written continuously at a user specified frequency. However, within the Data Route module users gain the ability to use another OAS tag to set the frequency for continuous data write, allowing for a dynamic frequency tailored to moment-by-moment facility requirements.
Then there are three completely new options for triggering a data-write that are not at all available in the simpler ‘Enable Write to Tag’ feature. The first of these is an event-driven trigger which involves selecting another OAS tag of either a Boolean or Integer data type. Data Route can then be triggered based on when a Boolean tag changes from true to false, false to true, or both. When using an Integer Tag, Data Route will be triggered any time the tag value changes to a non-zero integer. This has a variety of different operational use cases from making automatic adjustments in response to certain alarms, to automated production scaling based on user input or data from other automated systems.
Secondly, data-write can be triggered on a change in value of the destination tag as opposed to the more typical configuration of routing data when there is a change in a specified source tag. This is useful particularly when it is important that some piece or data or control parameter constantly holds a certain value or matches some other one, such as ensuring a furnace stays at a given temperature or that all conveyer belts are running at identical speeds.
Lastly, the most simple and straightforward of these configurations is simply initiating a data route at a given time of day. Great for regularly communicating telemetry data or resetting device configurations on a scheduled basis.
Users can create any number of Data Route groups as they please, and any Data Route group can be enabled or disabled using a separate Boolean tag. This means it is even possible to have Data Route for a group of tags configured one way for a certain part of a day and another way for a different part of the day without any user intervention at all! Test and benchmark operations by creating a Data Route group to write static data in order to emulate process conditions or write dynamic data when tag values change to set up device handshaking. Data Route gives users the breadth of capabilities they need to unleash their creativity and address operational challenges in a myriad of ways. Visit the Knowledge Base for further guidance on configuring a Data Route group.
IoT Tag Publish
OAS Data Route provides incredible capabilities in the way of transferring data between multiple plant devices. But what if data needs to be published to cloud platforms? This is where users can make use of the Bulk Tag Publish feature of OAS’ IoT Drivers. OAS supports publishing data to MQTT, Azure IoT Data Hub, Azure IoT Event Hubs, Kafka, and AWS IoT Gateway. (OAS is also an MQTT Client.) Data is published in a customizable JSON format or, optionally, to Avro Schema to Azure IoT Event Hubs.
Configuring the desired IoT Hub is easy, and it is where users have several options for how data should be published to the IoT Hub. Selected tags can be bulk published to the IoT Hub continuously, based on a user specified frequency; on an event-driven basis where another OAS tag with a Boolean data type can be used to trigger the publish; or at a specific time of day.
When using event-driven publish, like the previous applications, the publish can be triggered on the change of a tag from true to false, false to true, or both. Users can also elect to publish only the latest values of the tags included in the created list; when enabled, only the most recent value of any given tag will be included in the publish, otherwise, all values held by the tag since the previous publish will be included. If it is not desired to publish tags that have seen NO change in value since the last publish, then these can be excluded. Whether or not all the tags published will belong to a single topic by default or be separated into multiple distinct topics is also up to the user.
Using IoT Tag Publish in conjunction with Data Route means it is possible to coordinate data flow even between two or more remote devices. This allows for powerful coordination not just between all the operational assets of a single plant but, potentially, an entire enterprise.
Networking
All three Data Route features support communications to remote OAS Engines running on Windows or Linux. Tag-to-Tag Transfer can send data to remote tags on other systems, IoT Publish can receive data from remote systems, and Multiple Tag Transfer can both send and receive data from any number of remote OAS Engines where the Data Route feature is enabled. Read more on OAS Networking.
