As enterprise infrastructures evolve and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems become more distributed, businesses must decide between edge computing vs. cloud computing, or how to best combine the two. Understanding the nuances of cloud computing and edge computing can help you build a more efficient, responsive, and cost-effective IIoT platform.
 What is Edge Computing?
What is Edge Computing?
In edge computing, critical data processing occurs at the data source rather than in a centralized cloud-based location. Other terms sometimes used to describe edge computing include ‘fog’ computing and grid computing.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) relies on data from many sensors, controllers, and attached servers, often across multiple, remote locations. Certain data processing tasks are best performed ‘at source’ rather than in the cloud.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the internet. Instead of processing data locally, businesses send it to centralized data centers in the cloud for handling.
This model allows for scalable computing power, centralized management, and advanced analytics capabilities. In IIoT environments, cloud platforms are well-suited for storing large datasets, running machine learning models, and powering enterprise-wide dashboards.
Why Cloud-Only Architectures Fall Short for Real-Time IIoT Data
When it comes to cloud vs edge computing, it’s important to understand that cloud solutions alone are not always ideal for real-time IIoT applications.
Here’s why:
- Traditional cloud computing pushes data to a central server and pulls it back down to clients, which introduces latency.
- For real-time IIoT use cases, this delay can mean unreliable data delivery and lower accuracy.
- Bandwidth costs escalate as large volumes of data are transferred to the cloud.
- Network outages or low-quality connections impact performance and availability.
While cloud computing is effective for certain workloads (like document storage or content delivery) it lacks the responsiveness required for time-sensitive industrial applications.
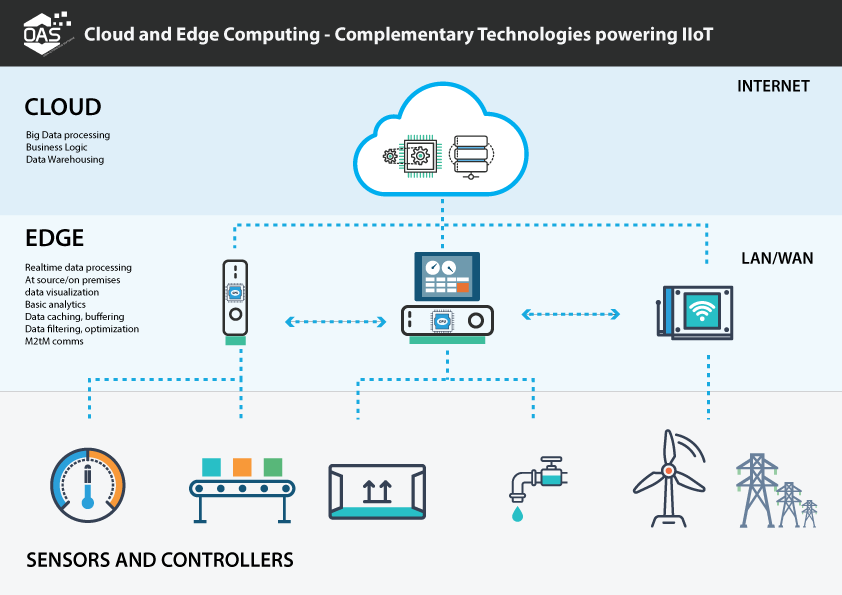
Edge vs Cloud Computing: A Side-by-Side Comparison
Understanding the different strengths of edge and cloud computing helps clarify when to use each architecture.
Edge Computing Capabilities
- Basic data visualization
- Basic data analytics and short-term data historian features
- Data caching, buffering, and streaming
- Data pre-processing, cleansing, filtering, and optimization
- Some data aggregation
- Device to Device communications/M2M
Cloud Computing Capabilities
- Complex analytics
- Big Data mining
- Sources of business logic
- Machine learning rules
- Advanced visualizations
- Long term data storage/warehousing
Real-World Example: Edge Computing in Action
Imagine a field technician servicing a remote wind turbine. With edge computing, they can instantly access key diagnostic data, even in areas with limited cellular connectivity. The turbine’s local IIoT gateway provides the required compute power on-site.
More in-depth analysis and historical trend reports, however, are handled later via the cloud computing platform. This hybrid approach ensures speed at the edge and analytical power in the cloud.

The Business Case for Edge Computing
The business case for edge computing is driven by cost savings in computing power and bandwidth as well as its ability to provide faster and more accurate access to automation data at its source.
For many IIoT applications, edge computing is the reliable and cost-effective way to ensure data quality, freshness, accuracy, and speed of delivery. Other factors, such as the quantities of data transferred and bandwidth costs, will determine the ultimate mix of cloud and edge services.
Cloud Computing vs. Edge Computing: Which Is Right for You?
Edge computing and cloud computing are complementary architectures that come together to create powerful IIoT platforms. One does not replace the other.
The best IIoT solution for your business will likely be a mix of the two architectures. Deciding which computing tasks should happen in the cloud or at the edge requires careful analysis of your business needs. Software providers like Open Automation Software are ideally placed to provide the software infrastructure for creating a world-class IIoT solution, as well as providing advice on how to best design your edge computing platform.
 Download a fully functional 30-day trial of the Open Automation Software platform.
Download a fully functional 30-day trial of the Open Automation Software platform.
Complete the form below and get instant access to a full-featured trial version of Open Automation Software.

